* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Some things to consider before we start
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
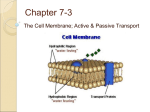
Some things to consider before we start Molecules in solids, liquids, and gases are always moving. In which state of matter are molecules moving the fastest? • Gas Slowest? • Solid • http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/states_of_matter/ Some things to consider before we start Substances must go through the cell membrane in order to get in or out of a cell. Some things to consider before we start • What substances need to go IN to a cell? – Water, food/glucose/, oxygen • What substances need to go OUT of a cell? – Wastes, carbon dioxide • Cell Membrane Movie CELL MEMBRANES • … are selectively permeable, which means that they allow some substances to pass through but not others. • Selective means “choosy” and • Permeable means “to go through” Demonstration: Smelly Balloons Record your observations about the balloons’ smell as they are passed around. Discussion Q’s: 1. How do the smells get out of the balloon? 2. How does your nose detect the smell? 3. Describe how the molecules are moving inside the balloon? 4. How is the balloon similar or different to the cell membrane? Diffusion • Molecules will always move from an area where they are more CONCENTRATED to an area where they are less CONCENTRATED. This is called diffusion. What does concentrated mean? • How many particles are packed in an area Diffusion continues until the molecules of a substance are evenly distributed in an area. • This state of “evenly spread” is called equilibrium. • Do molecules stop moving once equilibrium is reached? • NO http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.html http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP1903 Diffusion by Brainpop … is a special kind of diffusion that is very important to living things. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. This is the manner in which water gets into and out of cells. Animation: How Osmosis Works http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_osmosis_works.html • Water molecules will naturally flow from an area in which the water molecules are in greater numbers to an area where they are in fewer numbers. http://www.biologycorner.com/bio1/diffusion.html • Which way are water molecules moving when a plant begins to wilt? • Out of the cells Passive transport requires no ENERGY from the cell. Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport. Molecules in the cell membrane called transport proteins help to move LARGER molecules into or out of the cell. This still does not require energy. Think of this as being like taking a ferry ride without having to pay. This is called Facilitated transport facilitated transport http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/ani mation__how_facilitated_diffusion_works.html Active transport requires ENERGY and uses transport proteins in the cell membrane. Used when cells need to move substances from areas of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This is the opposite of DIFFUSION and requires energy. Other types of active transport endocytosis o Endocytosis occurs when VERY LARGE THINGS need to move INTO a cell. o A vesicle fuses to the cell membrane and then releases an object into the cell. o A white blood cell “eating” a BACTERIA would be an example of endocytosis. o What does “endo” mean? “IN” Exocytosis o Occurs when VERY LARGE molecules need to move OUT of a cell. o A vesicle fuses to the cell membrane and then releases an object out of the cell. o An example of exocytosis is when proteins packaged by the GOLGI BODIES need to move out of the cell, to get to another cell. o What does “exo” mean? OUT OF Let’s get some practice: Tell if each of the following as diffusion, osmosis, facilitated transport, active transport, endocytosis, or exocytosis. • Large waste molecules stored in vacuoles need to be moved out of a cell: • exocytosis Water concentration outside a cell is 85%. Water concentration inside the cell is 70%. Water flows into the cell: • Osmosis 85% 70% • You can smell the cookies baking in the oven even before you enter the kitchen: • Diffusion The concentration of Na ions outside the cell is 10%. The concentration of Na ions inside the cell is 25%. Na ions move into the cell. • Active Transport 25% 10% A one-celled organism “eats” another one-celled organism: • Endocytosis • Glucose molecules are helped to move into the cell by transport proteins in the cell membrane, but no energy is used to do this: • Facilitated transport