* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oceanography notes:
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Demersal fish wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
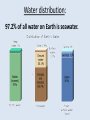
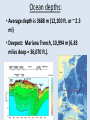
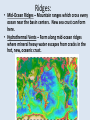
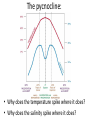
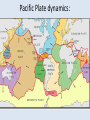
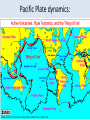
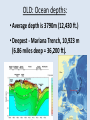
Oceanography notes (part 1): Ocean size and names • Nearly 71% of the Earth’s surface is covered by oceans. • 4 major oceans ranked by size: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic. (Southern Ocean [proposed] = considered an extension of Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, and covers the waters that surround Antarctica) Water distribution: 97.2% of all water on Earth is seawater. Ocean depths: • Average depth is 3688 m (12,100 ft. or ~ 2.3 mi) • Deepest: Mariana Trench, 10,994 m (6.83 miles deep = 36,070 ft.). Currents: • Currents in the ocean can be affected by differences in wind / air pressure, temperature, Coriolis effect, salinity and density. Sea floor features: Coastal features: • Continental Margin = transition from continent to nearby ocean floor (next two combined) • Continental Shelf – Part of the continent which is under water (a shallow area). – Significant due to large amounts of fish, minerals, oil/gas, sand/gravel in this area. • Continental Slope – The edge of the continent; ocean drops off to deep water. Continental slope parts: –Submarine Canyons – Canyons cut into the continental slope by turbidity (sediment), currents / earthquakes (mud, sand, and water). –Continental Rise – A gently sloping area at the base of the slope. Formed by turbidity flows, may be miles thick. Ocean floor features: • Abyssal Plains – The bottom, 10,000 to 20,000 feet deep. They are the flattest places on the planet as sediments have smoothed out the otherwise irregular ocean floor. • Abyssal Fans – Fan shaped deposits at the end of many large rivers. continental shelf continental slope continental rise continental shelf island guyot mid-ocean ridge seamount continental slope Other seafloor features: • Sea Mounts – Submerged volcano peaks; volcanoes that haven’t yet reached the surface to become islands. • Guyots – Flat top seamounts, tops were cut off by wave action. Ridges: • Mid-Ocean Ridges – Mountain ranges which cross every ocean near the basin centers. New sea crust can form here. • Hydrothermal Vents – Form along mid-ocean ridges where mineral heavy water escapes from cracks in the hot, new, oceanic crust. Final features: • Trenches – Deep troughs near continents. Where sea floor crust is pushed down into the earth and melted. • Fracture Zones – Where mid-ocean ridges are broken by faults. Oceanography notes (part 2): Ocean study: • Little was known before Sonar, invented in 1920’s. (Sonar = SOund Navigation And Ranging) • The world’s largest wilderness. Sea Water: • Salinity – The dissolved solids in seawater. 3.5% of seawater is dissolved minerals / salts • Measured in parts per thousand (ppt) “32 – 37 o/oo” [compare to %] • Salts in seawater: Sodium Chloride (NaCl or ions) = ~ 85% What Affects Salinity? • Salinity increases with land runoff, evaporation, volcanic eruption, formation of sea ice. • Salinity decreases with precipitation, melting of icebergs, sea ice. The pycnocline: • Why does the temperature spike where it does? • Why does the salinity spike where it does? Currents: • Currents in the ocean can be affected by differences in wind / air pressure, temperature, Coriolis effect, salinity and density. • Tsunami source?? Pacific Plate dynamics: Pacific Plate dynamics: OLD: Ocean depths: • Average depth is 3790m (12,430 ft.) • Deepest - Mariana Trench, 10,923 m (6.86 miles deep = 36,200 ft).