* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ocean Floor Power Point
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
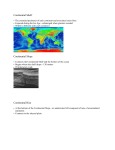
Ocean Landforms The Ocean Floor Revealing the Ocean Floor • If you could travel to the bottom of the ocean, you would see the world’s largest mountain chain and canyons much deeper than the Grand Canyon. • How can the ocean floor be mapped? Revealing the Ocean Floor Sonar (stands for Sound Navigation and Ranging) Invented in the 1920s Primary instrument for measuring depth Reflects sound from ocean floor Revealing the Ocean Floor Use of satellites for mapping Employs satellites equipped with radar altimeters Scientists are able to measure the direction and speed of ocean currents. Measure the different heights of the ocean surface to make maps of ocean floor. Can cover more territory using satellites rather than ship sonar. Continents Edge • Called the continental margin • Three parts –Continental shelf –Continental slope –Continental rise Continental Shelf • Begins at the shoreline • Continues until it begins to slope more steeply downward • Depth can reach 200 meters • This is what you walk on at the beach. Continental Slope •Begins at the edge of shelf and continues to flattest part of ocean floor •Depth ranges from 200 meters to 4000 meters •Continent ends at bottom of continental slope Continental Rise • Slopes more gently • Made of sediments that come off the shelf • Like underwater avalanches of sediment and water Abyssal Plain • Broad, flat portion of the deep-ocean floor. • Covered with mud and remains of marine organisms. • Average depth is 4,000 meters Mid-Ocean Ridges • Mountain chains formed where tectonic plates pull apart. • Pulling motion creates cracks in the crust called rift zones. • Rift Valley forms between mountains in the mid-ocean ridge. Seamounts • Individual mountains of volcanic material. • If a seamount builds up above sea level, it becomes an island. • A guyot is a flat-topped seamount. Actual footage of an erupting underwater volcano. Ocean Trench • Seemingly bottomless cracks in the ocean basin. • Formed where one oceanic plate is forced underneath another plate. • Most famous: Marianas Trench