* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download breedingandfertilisationlesson6
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
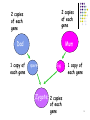
Standard Grade Biology Breeding and Fertilisation and Genotype By the end of this lesson: You should be able to: Know what a genotype is Know what alleles are Know the difference between homozygous and heterozygous 2 Genes come in pairs All the cells of an organism have TWO copies of every gene (except sex cells). Humans have 46 chromosomes, but these exist in 23 pairs 3 What happens at fertilisation? Sex cells are also known as GAMETES Gametes do not have 2 copies of each gene, but only one When a male sex cell fuses with a female sex cell at FERTILISATION the ZYGOTE has 2 copies of each gene (one copy from mum and one from dad) 4 2 copies of each gene 2 copies of each gene Dad Mum 1 copy of each gene sperm Egg 1 copy of each gene Zygote 2 copies of each gene 5 Genotypes We said earlier that different characteristics can have different PHENOTYPES (this describes the way the characteristic looks) The genes for a particular characteristic can give different instructions Different forms of the same gene are called ALLELES 6 Genotypes The alleles of a gene are represented by letters The DOMINANT allele is represented by a CAPITAL letter The recessive allele is represented by a SMALL letter 7 Examples Hair colour, Blonde is recessive to brown B = Brown allele b = Blonde allele Height in pea plants, Tallness is dominant to dwarfness T = Tall allele t = Dwarf allele 8 Genotype For each characteristic, we have 2 alleles One came from Mum and the other from Dad! The two alleles present in an organism are known as its GENOTYPE 9 Summary GENOTYPE = The genes possessed by an individual PHENOTYPE = The physical appearance of an individual 10 Examples Tallness (T) is dominant to dwarfness (t) A tall pea plant could have the genotype TT or Tt A dwarf pea plant could only be tt 11 Examples Brown hair (B) is dominant to blonde hair (b) A brunette could have the genotype BB or Bb A Blonde could only be bb 12 Homozygous & Heterozygous If the two alleles are the SAME as each other (e.g. TT or tt) the genotype is described as HOMOZYGOUS. If the two alleles are different (e.g. Tt) then the genotype is described as HETEROZYGOUS If an individual is described at true breeding, it means they are HOMOZYGOUS 13 Task Insert and Complete the “Passage of Genes” diagram from your diagram pack into your jotter. Use the words “rough” or “smooth” to describe the guinea pig coat colour. 14 Task 1. 2. 3. Answer the following questions in sentences in your jotter What is the phenotype of the F1 guinea pig? Use letters to show the genotype of the F1 guinea pig. From this information which phenotype do you think is dominant? 15 Can you do it? Can you answer the following? What is a genotype? What are alleles? What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous? 16