* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 5 – Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nerves The Spinal Cord
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Edward Flatau wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
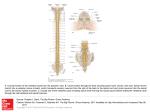
BMA1901HUMANSTRUCTUREANDFUNCTION Module5–SpinalCordandPeripheralNerves TheSpinalCord Objective1:Describethegrossanatomy,protectionandinternalstructureofthespinal cord TheSpinalCord Thespinalcordisstructurallyandfunctionallyintegratedwiththebrain. TheSpinalCord: • • • • Iscomposedofinterneurons(receiveandprocess–relay-relaycommands) Receivesanddirectsincomingsensoryinformationtoprocessingcentresinthebrain Receivesandrelaysmotoroutputfromthebrain Initiatesspinalreflexes TheVertebralColumn • Thespinalcordisencasedwithinthevertebralcanal,formedbyalignmentof multiplevertebralforamen. GrossAnatomyoftheSpinalCord • • • • • • Approx.42cmlong,14mmwide ExtendsfromforamenmagnumtoL2inadultsandL4inchildren Terminatesinaconeshapedstructureàfibrousconnectivetissueextendingfrom theconusmedullaristoanchorthespinalcordtothecoccyx Dividedinto31segments: àCervical(C1–C8) àThoracic(T1–T12) àLumbar(L1–L5) àSacral(S1–S5) àCoccygeal(Co1) Lumbar,sacral,andcoccygealsegmentsofthespinalcordaresqueezedintothe conusmedullaris(coneshapedend) Eachspinalsegmentisassociatedwithapairofspinalnerves(31pairs) SpinalNerves • Shortnerves BMA1901HUMANSTRUCTUREANDFUNCTION Containbothsensory&motoraxons (mixednerves) Connecttothespinalcordatoneend andbranchtoformperipheralnervesat theother Spinalnervesattachtothespinalcord bypairednerverootsàventraland dorsalroots(mixednerves) • • • Ventralroot-containstheaxonsofmotor neurons(issuesmotorcommandsto effectorglandsandmuscles) Dorsalroot-containstheaxonsofsensoryneurons(relayssensoryinputfrom receptorstothespinalcord) o Cellbodiesofsensoryneuronsliewithinthedorsalrootganglion WhilethespinalcordendsatL2,thelumbar,sacralandcoccygealnerverootextend inferiorlytoreachthepointofspinalnerveexitfromthevertebralcolumn.Thesenerve rootsarecollectivelycalledthecaudaequine. ProtectionoftheSpinalCord Thespinalcordisprotectedbythe • Vertebralcolumn • Spinalmeninges(spinalduramater,arachnoidmater,piamater) • Cerebrospinalfluid TheSpinalMeninges • Theduraarethearachnoidmaterextendbeyondtheandofthespinalcord(at L2)tothelevelofS2) • Alumbarpuncture(spinaltap)involvestheinsertionofaneedleintothe subarachnoidspacebeyondL3 • Thisprocedure o Doesn’tdamagethespinalcord o IsusedtowithdrawCSFforfluidfordiagnostictestingoftoreduceICP o Maybeusedtoadministermedication • • • • • Arecontinuouswiththebrainmeninges(dura,arachnoidandpiamater) ContainCSFwithinthesubarachnoidspace Providestabilityandprotectionforthespinalcord Containbloodvesselsthatdeliveroxygen&nutrientstocordtissue Areseparatedfromthevertebralcolumnbyanepiduralspace o Filledwithadiposetissueandbloodvessels o Siteodanaestheticinjection BMA1901HUMANSTRUCTUREANDFUNCTION • Aresecuredtothespinalcordbydenticulateligaments TheMeninges Bone(skullof vertebralcolunm) EpiduralSpace(spinal cordonly) DuraMater SubdrualMater(fluid andbloodvessels) ArachnoidMater SubcranialSpace(CSF andBloodvessels) PiaMater NervousSystem MicroscopicAnatomyoftheSpinalCord Thespinalcordconsistsofgreyandwhitematterandisdividedintotheleftandtheright halvesbytwogrooves 1. Anterior(ventral)medianfissure 2. Posterior(dorsal)mediansulcus BMA1901HUMANSTRUCTUREANDFUNCTION Objective2:Describetheorganisationandfunctionofthegreymatter. Greymatter • • • • Composedofneuroncellbodiesanddendritesofneuronsunmyelinatedaxonand neuroglia Variesinsizeanshapedownthespinalcord Surroundsthecentralcanal Organisedintogreyhorns o Posterior(dorsal)greyhorns o Lateralgreyhorns(thoracicandlumbarregionsonly) o Anterior(ventral)greyhorns • • • Greycommissuresàaxonscrossover(decussate) Fromonesideofthecordtotheother Thecellbodiesofneuronswithinthegreymatterareorganisedintofunctionalgroups callednuclei: Sensorynuclei • Containthecellbodiesofspinalcordinterneurons o Receiveandintegratesensoryinformationenteringthespinalcord Motornuclei Containthecellbodiesofmotorneurons • o Receivemotoroutputissuedbythebrain o Relaymotoroutputtoperipheraleffectors o Generatemotoroutputthatmediatesspinalreflexes Objective3:Describetheorganisationandfunctionofthewhitematter. WhiteMatter • • Theaxonwithinthewhitematterarefunctionallyorganisedintospinaltracts Spinaltracts o o o o Subdivisionofawhitecolumn Spinalcordsectionofamulit-neuronpathway Collectionofaxons Theaxonsineachtractsarefunctionallythesame - Thesametypeofinformation Thesamedirection