* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell respiration review
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
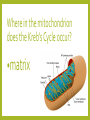
CELL RESPIRATION REVIEW Get yourself a whiteboard, marker and tissue. What is the end product of glycolysis? and how many? pyruvate two How many carbons does pyruvate have? Three (3) To where is the pyruvate transported? •Inside mitochondrion What is removed from the pyruvate? Name of this reaction? •CO2 •decarboxylation What is added to the acetyl group? •Coenzyme A When acetyl-CoA joins with 4C oxaloacetate, what is formed? (6C) citrate/citric acid Where in the mitochondrion does the Kreb’s Cycle occur? •matrix For one glucose, how many turns of the Citric Acid Cycle are taken? •two (2) How many ATP’s are made in the Kreb’s Cycle? (per one glucose) •two (2) How many CO2’s are removed in the Kreb’s Cycle? (per one glucose) •four (4) What is done to the NAD+’s in the Kreb’s Cycle? “They are _____.” •reduced What is the other electron acceptor in the citric acid cycle? •FAD When the FAD is reduced, what does it become? •FADH2 Where is the electron transport chain located? embedded in inner membrane (of mitochondrion) What molecule(s) deliver electrons to ETC? •NADH and FADH2 What happens to electrons as they move down the ETC? •they lose energy How is this energy used? •To pump protons/H+’s To where are the protons pumped? •intermembrane space When protons are pumped, what is created? •proton gradient What is the final electron acceptor? •Oxygen/O2 What else does the oxygen accept? Making what molecule? •protons •Water/H2O Through what molecule do the protons flow back into the matrix? •ATP synthase/synthetase What does ATP synthase make? How many (per glucose)? •ATP •28/32/a lot! What is the name of this process? •chemiosmosis What process(es) is/are anaerobic? •glycolysis •fermentation What process(es) is/are aerobic? •Kreb’s/Citric Acid Cycle and oxidative phosphorylation The End!!