* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Theory - Science with Mrs. Stevenson
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
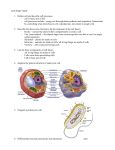
Objectives ●List scientists who contributed to the cell theory ●List the components of the cell theory ●Compare prokaryote and eukaryote cells ●Label a plant and an animal cell ●Know the functions of cell organelles The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. *Why is the Cell Theory called a Theory and not a Fact? Early Contributions ● Robert Hooke - First person to see cells, he was looking at cork and noted that he saw "a great many boxes. (1665) ● Anton van Leeuwenhoek - Observed living cells in pond water, which he called "animalcules" (1673) Leeuwenhoek saw these things in pond water. What did he call them? ●Theodore Schwann - zoologist who observed tissues of animals had cells (1839) ●Mattias Schleiden - botanist, observed tissues of plants contained cells ( 1845) ●Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He predicted that cells come from other cells. (1850 ) Checkpoint What was their contribution? Hooke Leeuwenhoek Schwann Schleiden Virchow The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of _____ 2. Cells are the basic unit of _______ and ______ 3. Cells come from _______________ cells. Cell Features ALL cell have these parts ●Ribosomes – make protein for use by the organism ●Cytoplasm – fluid material within cell ●DNA – genetic material ●Cytoskeleton – internal framework of cell ●Cell Membrane – outer boundary, some things can cross the cell membrane Comprehension Checkpoint Answer true or false 1.Robert Hooke was the first person to see cells. 2.Bacteria cells have a cell membrane. 3.The Cell Theory was developed by a single scientist. 4.Plant cells have cytoplasm. 5.Cells taken from fungi do not have DNA. 6.Cells can only come from pre-existing cells. 7.It only took five years to develop the Cell Theory. Prokaryote Cells ● The first cells to inhabit the earth ● Simple cells ● Bacteria ● These cells do NOT have a nucleus, their DNA is circular and floats in the cytoplasm Some bacteria have a taillike structure called a flagella, that helps it to move. A capsule surrounds some bacteria and helps them avoid the body’s immune system Bacteria Images Bacteria that causes Anthrax CHECKPOINT LABEL THE BACTERIA Bacteria belong to a group of cells that do not have a ____________ Eukaryotic Cells Cells found in plants, animals, protists, and fungi The cell is composed of 4 main parts: 1.Cell membrane 2.Cytoplasm 3.Nucleus – “control center” of cell, DNA 4.Organelles – small structures that carry out specific functions (“little organs”) Nucleus ● Usually found at center of cell ● Has a nuclear membrane & nuclear pores ● Contains cell’s DNA in one of 2 forms o chromatin - DNA and proteins, becomes... o chromosomes - during cell division Nucleolus - which makes the cell’s ribosomes True of False 1. All cells have a nucleus. 2. All cells have a cell membrane. 3. Eukaryote cells are the only cells to have a flagellum. 4. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA. 5. Chromatin will become chromosomes. 6. The nucleolus makes the cell’s DNA. Cell Organelles Mitochondria – cell’s energy center; turns food into a chemical energy called ATP The mitochondria is sometimes called the “powerhouse” of the cell Cell Organelles Golgi Apparatus – processes, packages and secretes proteins. It is comparable to a factory or a post office. *A vesicle forms with Golgi to transport substances outside cell. Cell Organelles Lysosome – Contains digestive enzymes, breaks things down, "suicide sac” Endoplasmic Reticulum – Transport, "intracellular highway". -Rough ER contains many ribosomes & is involved in protein synthesis -Smooth ER no ribosomes Vacuole – storage area for water and other substaces, plant cells usually have a large central vacuole Protein Production The cell is like a factory. Its product is protein which goes to body to serve different functions. 1.DNA has instructions to build protein 2. Instructions are sent to ribosomes 3.The ribosomes build protein and sends it through ER 4.The proteins go to golgi where they are packaged for export THE ANIMAL CELL Cheek Cells Seen Through Microscope NAME THE PARTS Plant Cells ●CELL WALL – provides additional support ●CHLOROPLASTS – contain green pigment, photosynthesis ●CENTRAL VACUOLE – large water container PLANT CELL Can you identify the parts? Anacharis Cells Viewed With a Microscope Animal Cell vs Plant Cell CELL MEMBRANE ● Selectively permeable ; it regulates what comes into the cell and what leaves the cell ● It is composed of a double layer of phospholipids with proteins embedded throughout