* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3, Section 4 Notes (p.97-103)
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
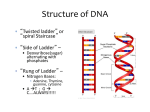
Chapter 3, Section 4 Notes (p.97-103) I. The Genetic Code a. Proteins determine traits (size, shape, color, etc.) b. Chromosomes are made of DNA c. DNA molecules made of four nitrogen bases i. Adenine ii. Thymine iii. Guanine iv. Cytosine d. Genes are made up of a series of nitrogen bases e. Order of nitrogen bases determines the protein that is produced II. How Cells Make Proteins a. Protein synthesis: the production of proteins i. Chromosomes found inside nucleus in a cell ii. Proteins are produced in ribosomes (outside nucleus) b. RNA – ribonucleic acid i. Made of one strand of nitrogen bases ii. Contains uracil INSTEAD of thymine c. Types of RNA i. Messenger RNA – copies coded message from DNA (in nucleus) and carries it to ribosome (in cytoplasm) d. Transfer RNA – carries amino acids to the ribosome and adds them to a growing protein e. Translating the Code i. DNA molecules “unzip” between base pairs, creates messenger RNA to pair up with DNA strand, genetic info. is transferred from the DNA to the messenger RNA ii. Messenger RNA travels to cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome (where protein production begins); ribosome moves along the messenger RNA strand iii. Transfer RNA attaches to messenger RNA by matching up with three-letter codes of bases; amino acids are added to the growing protein chain iv. Protein chain continues to grow until the ribosome reaches the “stop” code; the ribosome releases the completed protein III. Mutations a. Mutations: cause cells to produce an incorrect protein during synthesis. The protein may cause an organism’s traits to change because of this i. Only mutations occurring in a parent’s sex cells can be passed on to the offspring. b. Types of mutations: c. i. Single nitrogen bases being substituted for other bases (can occur during DNA replication) ii. Chromosomes fail to separate correctly (offspring could end up with too many or too few chromosomes) Effects of Mutations i. Mutations can be helpful, harmful, or no positive or negative effect on the organism ii. Mutations are harmful when they reduce the organism’s chance for survival or reproduction iii. Helpful mutations improve an organism’s chance for survival