* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tonicity
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
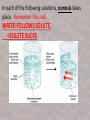
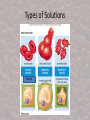
Describes the ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water. It depends on the concentration of a solute. Solutions • Remember that a solute is dissolved into a solvent to make a solution. Solute + Solvent Solution Types of Solutions • There are 3 types of solutions. This is based on a comparison of the concentration of solute (the part being dissolved) in each. Imagine placing a cell into a solution and comparing the concentrations of solute in both. Solution Cell Types of Solutions 1) Isotonic Solution – The concentration of solute and water in the cell is equal to outside the cell. Water is moving = into and outside of the cell, EQUALLY! Draw and label the pics. Solution Normal in animal cells Cell Flaccid (not firm) in plants In each of the following solutions, osmosis takes place. Remember this rule: WATER FOLLOWS SOLUTE, =SOLUTE SUCKS Remember: Solute Sucks draw and label the pics in your IAN Types of Solutions 2) Hypotonic Solution – concentration of solute is less and water greater outside the cell. Water will follow the solute and move into the cell to try and create a balance, equilibrium, homeostasis. The cell will swell up. Cell An animal cell will undergo cytolysis=lysed=burst (draw, label pics) A plant cell has a cell wall so it will not burst, but will be come very TURGID, they swell and are firm, Normal for plants. Types of Solutions 3) Hypertonic Solution – The concentration of solute is greater and concentration of water is less outside the cell. Water will move out of the cell to try and balance the concentrations so the cell will shrivel. Cell An animal cell will undergo crenation (shriveling) (draw, label pics) A plant cell has a cell wall that remains the same but the cytoplasm will shrivel inside the cell membrane, which is called plasmolysis (plasmolyzed). Types of Solutions flaccid