* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Candidate Gene Approach
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
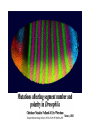
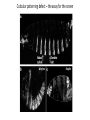
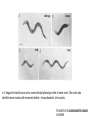
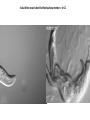
Lecture 5 Candidate Gene Approach - 1 BSE652 19-1-2017 To understand genetic basis of development “How genes might specify the complex structures found in higher organisms is a major unsolved problem in biology.” Sydney Brenner, 1974 – “THE GENETICS OF CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS” “To discern the genetic contribution clearly, the thing to do is to keep the environment constant and change the genes.” From the Gene to Behavior, Seymour Benzer, 1971 “This is not easy to do with human beings; they are notoriously uncooperative and unwieldy experimental subjects, particularly if one must wait generations for the results.” Seymour Benzer, 1971 To understand genetic basis of development Question There are 15-25,000 genes in a given multi-cellular organism. Which genes’ role should one study? Candidate gene approach 1. Mutate all genes, one gene at a time, to see which developmental process is being affected Saturation mutagenesis screen Drosophila as the model organism Morgan, Sturtevant ……………… A culture was started where the gene is named after the mutant phenotype, white C. elegans as the model organism Sidney Brenner, Sulston and Horvitz ……………… Mutants were named in series based on gross phenotype – unc, lin, lon etc. Zebrafish as the model organism Chuck Kimmel, Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard First vertebrate saturated mutagenesis screen, transparent embryo, very helpful for hematopoiesis research Mouse as the model organism Kathryn Anderson, Monica Justice Very difficult to conduct. However, some key genes were discovered using this approach. Nature, 1980 Outline of the crossing schemes used in the Heidelberg screen Please read about balancer chromosomes These are specific for specific chromosomes and prevent homologous recombination Balancer/balancer animals are dead Please remember that there is no meiotic recombination in drosophila males And drosophila stocks cannot be frozen for later use, it has to be continuously maintained The art and design of genetic screens: drosophila melanogaster Daniel St. Johnston VOLUME 3 | MARCH 2002 Compulsory reading Cuticular patterning defect – the assay for the screen Wingless Staufen Wild type Small Dumpy Long In C. elegans the tradition was not to name individual phenotype rather to name series. This screen also identified some mutants with movement defects – Uncoordinated or Unc mutants. THE GENETICS OF CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS S. BRENNER The lin mutants Vulval defect mutants identified Notch pathway members – lin-12 Large scale genetic screen in a small vertebrate: zebrafish Fig. 4. Examples of mutations with specific defects in the development of zebrafish embryos. AI! embryos shown are 24 hours-old. (A)Wildtype. (B) cyclops mutant with partial!y fused eyes (Hatta et a/.. 1993). (C) Wildtype. (D) cyclops mutant showing the absence of a floor plate (Hatta et al., 1993). (E) Wildtype, (F) no tail mutant which lacks a differentiated notochord, has no tai! and abnormally shaped somites (Halpern et al.,1993). (GI Wildtype, (H) spade tail mutant accumulates trunk somitic mesoderm precursor cells in the tail (Ho et al., 1990). Which genes will escape the scan? 1. Maternally supplied genes i.e. the reason why maternal effect screen had to be conducted separately. 2. Involved in patterning/differentiation of internal structures 3. Only first instance of essential function may be scored 4. Genes having redundancy