* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
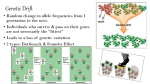
Bell Ringer 1. Silently Write the learning the targets off the board, into your notebook. 1. Take out your homework and have it ready to be turned in. 2. What is your understanding of natural selection? 3. What are the 3 requirements for natural selection to occur? Evolution How do we know it happens? Evidence? How do we know it happens? How does it happen?????? How do organisms evolve? Natural Selection “survival of the fittest” Microevolution and Microevolution • Changes a gene pool from generation to generation. – Gene pool: the total of all genes in the population Types of Microevolution 1. Gene Flow 2. Genetic Drift 3. Nonrandom Mating 2 1. Gene Flow: the exchange of genes due to migration • Mutations will occur over time. They are natural and produce genetic diversity that is needed for survival. How would this lead to the evolution of the population? Gene Flow in Plants Gene Flow in Humans 2. Genetic drift: the change in the gene pool of a population due to a random occurrence. Ex: Bottleneck Effect and Founder Effect Bottleneck = any kind of event that reduces the population significantly..... earthquake....flood.....disease.....etc.… Examples of Genetic Drift A) The Founder Effect: A founder effect occurs when a new colony is started by a few members of original population. Small population that branches off from a larger one may or may not be genetically representative of the larger population from which it was derived. Only a fraction of the total genetic diversity of the original gene pool is represented in these few individuals. • For example, the Afrikaner population of Dutch settlers in South Africa is descended mainly from a few colonists. Today, the Afrikaner population has an unusually high frequency of the gene that causes Huntington’s disease, because those original Dutch colonists just happened to carry that gene with unusually high frequency. This effect is easy to recognize in genetic diseases, but of course, the frequencies of all sorts of genes are affected by founder events. Examples of Genetic Drift B) Population Bottleneck: Occurs when a population undergoes an event in which a significant percentage of a population or species is killed or otherwise prevented from reproducing. •The event may eliminate alleles entirely or also cause other alleles to be overrepresented in a gene pool. EX. Cheetahs http://www.nytimes.com/1985/09/17/science/loss-of-gene-diversity-is-threat-to-cheetahs.htm l • An example of a bottleneck: Northern elephant seals have reduced genetic variation probably because of a population bottleneck humans inflicted on them in the 1890s. Hunting reduced their population size to as few as 20 individuals at the end of the 19th century. Their population has since rebounded to over 30,000 but their genes still carry the marks of this bottleneck. They have much less genetic variation than a population of southern elephant seals that was not so intensely hunted. 3. Non-Random Mating A situation where mates are chosen for one another or by another pre-determined factor. Leads to a loss of gene variability! Many plants self-pollinate, which is also a form of non-random mating (inbreeding). Sexual reproduction results in variation of traits in offspring as a result of crossing over in meiosis and mutations Genetic shuffling is a source of variation. Sexual selection occurs when certain traits increase mating success.