* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Drift - Ms. Stevens` Class
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
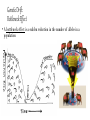
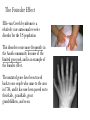
Genetic Drift • Random change in allele frequencies from 1 generation to the next. • Individuals who survive & pass on their genes are not necessarily the “fittest” • Leads to a loss of genetic variation • 2 types: Bottleneck & Founder Effect Genetic Drift: Bottleneck Effect • A bottleneck effect is a sudden reduction in the number of alleles in a population Genetic Drift: Founder Effect Occurs when a small part of a population moves to a new locale (or when the population is reduced to a small size because of some environmental change) The genes of the "founders" of the new society are disproportionately frequent in the resulting population. The smaller the new population, the more likely the allelic frequencies will differ from the original population. The Founder Effect The Amish community in eastern Pennsylvania was formed by ~200 German immigrants. It is a closed community, and members marry other Amish people. This creates a small gene pool (lack of genetic variability) for offspring, and a founder effect occurred because of this The Founder Effect Ellis–van Creveld syndrome is a relatively rare autosomal recessive disorder for the US population This disorder occurs more frequently in the Amish community because of the limited gene pool, and is an example of the founder effect. The mutated genes have been traced back to one couple who came to the area in 1744, and it has now been passed on to their kids, grandkids, great grandchildren, and so on. Founder Effect Original mainland population Some people from the mainland colonize an island Island gene pool is not as variable as the mainland’s Genetic Drift Examples Cheetahs are so closely related to each other that skin grafts from one cheetah to another do not provoke immune responses. This suggests an extreme population bottleneck in the past. Elephant Seals were reduced to 20 individuals in 1896. Now there are 30,000 individuals with no detectable genetic diversity. Overhunting almost caused extinction, now has begun to recover. Gene Flow Movement of alleles from one population to another. Occurs when individuals leave one population, join another, and breed. Immigration - alleles entering the gene pool Emigration - alleles leaving the gene pool Gene Flow Offspring of immigrated bird has a genotype of Hh Population A Selection pressure against recessive phenotype has created a homozygous homozygous dominant population Offspring of immigrated bird has a genotype of Hh Population B Selection pressure against dominant phenotype has created a homozygous recessive population (hh)