* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Cranial Nerves 1
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Craniometry wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
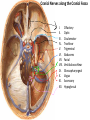
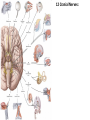
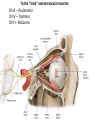
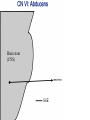
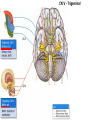
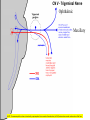
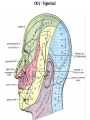
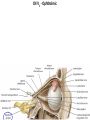
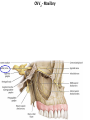
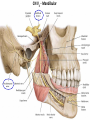
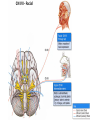
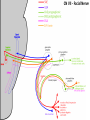
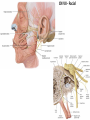
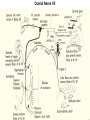
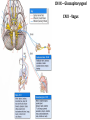
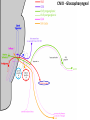
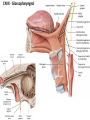
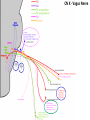
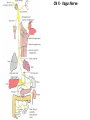
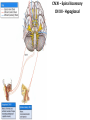
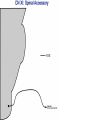
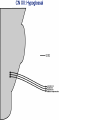
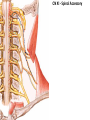
Gross Anatomy: Cranial Nerve Introduction (Grays, pages 807; 848-854) Vocabulary REVIEW CNS 1. Afferent: • sensory • primary afferents • axons entering the CNS • cell bodies in sensory ganglia • CN versus spinal nerves 2. Efferent: • motor • leaving the CNS • innervate skeletal muscle or viscera • visceral efferent pathways always involve 2 neurons [one in the CNS and one in a peripheral ganglia] Functional Components • • • • Special General Somatic Visceral – cranial nerves only; olfaction, vision, taste, balance and hearing – touch, pressure, proprioception, vibration, pain and temperature – body wall – smooth and cardiac muscle, glands and arrector pili General Somatic Afferent (GSA): General Visceral Afferent (GVA): Special Visceral Afferent (SVA): Special Somatic Afferent (SSA): General Somatic Efferent (GSE): General Visceral Efferent (GVE): Branchial Efferents (BE [SVE]): sensation from body wall sensation from viscera taste and olfaction DON’T NEED TO KNOW YET motor; to skeletal muscle motor to “viscera” motor (skeletal muscle from pharyngeal arches) CRANIAL NERVE SUMMARY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Accessory Hypoglossal CN I CN II CN III CN IV CN V CN VI CN VII CN VIII CN IX CN X CN XI CN XII (SVA) (SSA) (GSE, GVE-P) (GSE) (GSA, BE) (GSE) (BE, GSA, SVA, GVA, GVE-P) (SSA, SSE) (BE, GSA, SVA, GVA, GVE-P) (BE, GSA, SVA, GVA, GVE-P) (GSE) (GSE) Sensory Sensory Motor Motor Both Motor Both Sensory Both Both Motor Motor Cranial Nerves along the Cranial Fossa I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. IX. X. XI. XII. Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Accessory Hypoglossal 12 Cranial Nerves: To the “intra” and extraocular muscles: CN III – Oculomotor CN IV – Trochlear CN VI - Abducens Brain stem (CNS) Brain stem (CNS) Brain stem (CNS) CN V - Trigeminal CN V - Trigeminal Nerve Ophthalmic Maxillary NOTE: The mesencephalic nucleus is involved in proprioception from muscles of mastication, the TMJ, extraocular muscles and muscles of the face. CN V - Trigeminal CN V1 - Ophthalmic CN V2 - Maxillary CN V3 - Mandibular CN VII - Facial CN VII - Facial Nerve CN VII - Facial Cranial Nerve VII CN IX – Glossopharyngeal CN X - Vagus CN IX - Glossopharyngeal CN IX - Glossopharyngeal CN X - Vagus Nerve CN X - Vagus Nerve CN XI – Spinal Accessory CN XII - Hypoglossal CN XI - Spinal Accessory CN XII Hypoglossal