* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells!!
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
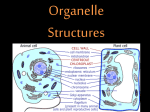
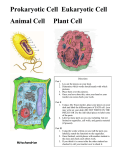
Cells!! Yay! We’re so excited!! I always wanted to learn about cells and stuff…really Mr. Mason…I’m not bored….this is awesome…just like cheese, which is also awesome…but not quite as awesome as cells. Well, except for melted cheese…and that fancy cheese at Costco…that stuff is pretty awesome. Wait…what was I saying??? Oh yeah…cells! Woohoo! Cell Theory • Life consists of cells • All cells are derived from pre-existing cells Cell Theory • Life consists of cells • All cells are derived from pre-existing cells – Cells are the smallest units of matter that exhibit all five characteristics of life Sizes of Cells • Most bacteria: 1-10 μm • Plant/animal cells: 10-100 μm • Can see with unaided eye down to 0.2mm (200 μm) • Largest cell? • Smallest cell? Sizes of Cells • Most bacteria: 1-10 μm • Plant/animal cells: 10-100 μm • Can see with unaided eye down to 0.2mm (200 μm) • Largest cell? • Smallest cell? egg Sperm • Relative size of cells Eukaryotic Cells • Defined by the presence of membranebound organelles (little organs). • Prokaryotes (bacteria) have an organelle (ribosome), but they are not membrane-bound Cell Membrane = phospholipid bilayer (or if you really want to sound smart, you can call it the Fluid Mosaic Membrane…or FMM) Functions of phospholipid bilayer • Protection • Transportation • Chem. reactions • Identification/commu nication Organelles that process info: • Nucleus and Ribosomes Nucleus • Storehouse for genetic code (DNA) • Synthesizes RNA and ribosomes Ribosomes • The site of protein synthesis • Composed of proteins and rRNA (3 types of RNA in cells – mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA…but we’ll get to that during 2nd semester) • Either free (proteins used in cytoplasm) or attached to E.R. (proteins inserted into membrane or used for export) Organelles that process energy • Mitochondria and plastids Mitochondria • Converts energy from organic compounds (such as glucose) into ATP • Have their own DNA (only organelle that has DNA other than the nucleus) Plastids • Chloroplasts – convert sunlight into glucose • Chromoplasts – give fruits and flowers their color (why?) • Leucoplasts – store starch (energy source) • Only found in plants The endomembrane system • Endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and lysosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum • Serves as an intracellular highway (carries materials around the cell) • Rough ER – covered in ribosomes, produces phospholipids and proteins – especially for export • Smooth ER – produces lipids (steroids, hormones, etc.), aides in cell detox, and stores necessary ions Golgi Apparatus • Processing, packaging, and secreting organelle • Modifies proteins for export, packages these (and other molecules) in vesicles (basically little cellular shipping containers) Lysosome • The dumpster of the cell • Contains hydrolytic enzymes that digest organic molecules Plant Cells – How are they unique? • Plants have: – Plastids – Vacuoles: large storage organelle – Cell wall covering phospholipid bilayer