* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biomolecules
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
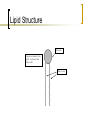
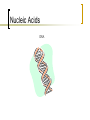
Biomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules are carbon based molecules made by living things. They can also be called macromolecules. Macro = large Micro = small Carbohydrates Carbohydrates: a molecule that is used by many plants and animals to store energy for a short time. Examples: Sugar, and Starch -ose means that something is a type of sugar. Example: Glucose, Lactose, Fructose Carbohydrates Some foods that contain a lot of Carbohydrates Pasta Bread Potato Lipids Lipids: molecules created and used by animals for long term energy storage, protection, and warmth. Fat on your body provides you with an extra layer for warmth if its cold It also protects your brain in case your head gets hit, absorbing the impact Examples: Fats Oils and Wax Lipids Things that contain lipids Cooking Oils Butter Candles Lipid Structure Glycerol Lipids are made of two parts. A glycerol and fatty acids Fatty Acids Protein Protein: the work horse of the biomolecules. These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many other things. Examples: Muscle on animals is mostly protein. Protein Some examples of protein Same Muscle Meats Note: The meat you eat is just the muscle of some animal. For example, beef is cow muscle. Proteins Proteins are polymers made of amino acids. Polymer- a molecule composed of many smaller units. Monomer – the smaller unit contained in a polymer. Proteins Enzymes, a type of protein, controls the rate of reactions. -ase means that something is an enzyme Example: Protease, Lactase, Amylase Example: Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose, a sugar. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids: store genetic information about an organism. Examples: DNA RNA DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the blueprint for most living things on earth. Those that don’t use DNA use RNA. Your DNA is unique and only an identical twin or clone will have the same DNA as you. Nucleic Acids DNA Review Questions Name the four Biomolecules: What are Carbohydrates used for? Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein, and Nucleic Acid To store energy for later use What are Nucleic Acids for? To store genetic information Review Questions What do lipids do for you? The store energy and help keep you warm. Give an example of a food where you would find protein. Any meat Review Questions Give an example of a food where you would find a lot of carbohydrates. Potato, bread, pasta, etc Give an example of food with a lot of lipids. Pizza, butter, any fatty food.