* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Ozone Depletion?
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
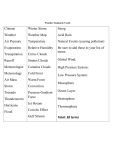
What is Ozone Depletion? Ozone layer depletion, is simply the wearing out (reduction) of the amount of ozone in the stratosphere. Unlike pollution, which has many types and causes, Ozone depletion has been pinned down to one major human activity. Industries that manufacture things like insulating foams, solvents, soaps, cooling things like Air Conditioners, Refrigerators and ‘Take-Away’ containers use something called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). These substances are heavier than air, but over time, (2-5years) they are carried high into the stratosphere by wind action. Depletion begins when CFC’s get into the stratosphere. Ultra violet radiation from the sun breaks up these CFCs. The breaking up action releases Chlorine atoms. Chlorine atoms react with Ozone, starting a chemical cycle that destroys the good ozone in that area. One chlorine atom can break apart more than 100,000 ozone molecules. Ozone layer depletion is best illustrated or explained with the Ozone Bucket Analogy. Click button below to have a look. The Ozone Layer This is simply a layer in the stratosphere containing a relatively high concentration of ozone. The earth's atmosphere is divided into several layers, and each layer plays an important role. The first region extending about 10km upwards from the earth's surface is called the troposphere. Many human activities like mountain climbing, gas balloons and smaller aircrafts operate within this region. The next layer, extending about 15-60 km is called the stratosphere. The ozone layer is mainly found in the lower portion of the stratosphere from approximately 20 to 30 kilometres (12 to 19 mi) above earth, though the thickness varies seasonally and geographically. The ozone layer protects the earth from the suns UV Rays. If the ozone layer is depleted by human action, the effects on the planet could be catastrophic. What is Ozone Hole? Top atmospheric researchers confirm that Ozone levels vary by season and latitude. Sometime in 1979, it was observed the there considerable Ozone depletion in the upper latitudes, Arctic and Antarctic. This massive stretch of ozone depletion (hole) is estimated to be about the size of America. Particularly in the antarctic, satellite images were released showing a disturbing thinning of the ozone layer. The phenomenon is what we usually call the Ozone hole, and it was most observed over the Antarctic every year during the spring. In the winter, temperatures drop below -78°C (-109°F) in the Poles (Antartic). Thin clouds form of ice, nitric acid, and sulphuric acid mixtures. Chemical reactions on the surfaces of ice crystals in the clouds release active forms of CFCs. This sets the ozone depletion going by spring, a lot of depletion has occurred. Why does the Ozone hole only occur in the Antarctic? Researchers say it is not only in the Antarctic, but in many places in other latitudes where populations are dense. It is believed that these places have cloud types that aid in the chemical reactions that cause ozone depletion. In spring, temperatures begin to rise, the ice evaporates, and the ozone layer starts to recover. Introduction to Climate change Many people make Climate Change and Global Warming a scary and difficult thing to understand, but it’s not. Scientists have warned that the world's climate has changed a lot, and has affected many living and nonliving things. Many places that were warmer are now getting colder, and many colder regions are getting much more colder or even warmer (know as Global Warming). For example, between 1901 and 2012, it is believed that the earth's temperature has risen by 0.89 °C. Rainfall amounts have also risen in the mid-latitudes of the northern hemisphere since the beginning of the 20th Century. It is also believed that sea levels have risen up to about 19cm globally, with lots of glaciers melting in addition. Some people do not believe that these are caused by human activities. They think it is all political and falsehood intended to cause panic among humans. Well, whatever it is, we would like to know more, and take a few good points from this confusion, and use them to make our world a better place to live. Important Climate Change Terms Climate This describes the total of all weather occurring over a period of years in a given place. It is the average weather condition of that place. Climate tells us what it’s usually like in the place where you live. For example, some countries like Cameroon, Ghana and Liberia are all in the tropical wet region of Africa. They have a very sunny, hot and wet climate all year round. However, there may be very different dayto-day weather conditions in each village or town in these countries. Weather Weather is all around us. Weather may be one of the first things you notice when you wake up. Weather describes whatever is happening outdoors in a given place at a given time. It can change a lot within a very short time. For example, It can be windy at night, rainy in the morning, hot and sunny at noontime, and even back to windy before sunset. It includes daily changes in rainfall, temperature and wind in a given location. Greenhouse Greenhouse is also another word you should know about. Have you ever seen a greenhouse? In some countries, people build a small glass house to plant crops in it. It is built to keep the sun's heat from escaping from the glasshouses. In a way, the earth is like a glasshouse. The earth has some very important gasses in the atmosphere that keeps us warm. Some of these gases are water vapour, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and methane. When the sun heats the earth, these gases keep the heat on the earth's surface. Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60°F colder. Effects of Climate change From what we have studied so far, you will notice Climate Change is an effect of Global warming. Global Warming also causes other things to happen that is not related to climate change. Let’s see these 4 good reasons. Global warming causes thermal expansion of land and water. It also causes ice sheets to melt in icy regions of the world and mountain tops. Large volumes of melted ice (water) then flows down into streams, rivers, lakes and seas. The result is rising sea and water levels, causing floods and massive destruction to low-lying towns and cities along water bodies. More on risisng sea levels here Research shows that global sea level rose about 17 centimeters (6.7 inches) in the last century, and the rate in the last decade is nearly double that of the last century. —Source: climate.nasa.gov Changing climate may also cause the weather to become more extreme, be it droughts or violent storms and heavy rain. Extreme changes in temperature makes people suffer breathing difficulties, head aches, body rashes and other illnesses. Climate change also distorts the natural habitats and lives of many plants and animals. For example, the survival of polar bears and penguins in icy regions are in danger, as they cannot survive anywhere else. Other plants and animals in hot regions will die if temperatures suddenly become too cold for them. Interesting facts on climate change Rising global temperatures A rising trend in global temperatures have been noticed after analyzing data for the last century. Scientists are aware that the difference in temperatures around the world is very wide apart, but after taking readings at specific locations over a long period of time, it is observed that there are more places warming up than cooling down. From 1900-2009, global average surface temperatures rose by approximately 0.7°C (1.3°F). It has also been noted that the rate of increase has risen in recent time. Source: Climate Change: Global Temperature, by LuAnn Dahlman, August 30, 2009 Carbon Dioxide Humans burning coal, natural gas and oils for manufacturing and transportation, since the Industrial Revolution, has produced and released massive carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. To put this in perspective, about 38% more CO2 has been released into the atmosphere, a value higher than has been measured for over 800,000 years. And yes, the amounts we release is still rising year after year. Source: Report by Caitlyn Kennedy, August 30, 2009, Climate Change: Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Ocean acidification The acidity of the earth's oceans is known to have increased by about 30%. This is a result of more CO2 emitted since the Industrial Revolution, being absorbed by the oceans. CO2 being absorbed by the upper layer of the oceans is increasing by about 2 billion tons per year.Source: PMEL Carbon Program, Ocean Acidification. Melting Glaciers Glaciers are massiveamounts of snow that have stayed long enough to harden into blocks of ice. Smaller blocks could be the size of a football field and larger once could be hundreds of kilometers long. Glaciers can move like rivers too. On the average, glaciers are losing ice at the rate of about 28 inches of water per year. Scientists revealed that even though only a small fraction of glaciers have been monitored since 1980, the trend is one that we need to be aware of.