* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Plasma Membrane aka the cell membrane http://sun
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
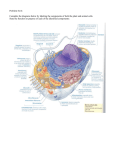
The Plasma Membrane aka the cell membrane http://sun.menloschool.org/~cweaver/cells/c/cell_membrane/ Cell membrane Facts • 1. Serves as "gateway + barrier for cell" • 2. Made up of phospholipids and proteins. • 3. Separates the contents of the cell from the external environment. • 4. It is extremely thin (you could stack 10,000 plasma membranes to equal the thickness of a piece of paper). The Cell membrane functions to: • Control what goes in and out of a cell. • Anchors the cytoskeleton to help provide shape. • Attaches to a substrate outside of the cell or to other cells to help form tissues • Controls the transportation of substances across the membrane by using proteins as carriers and channels • Contains receptors that allow cells to communicate through chemical messages • Contains recognition proteins which help identify the cell, so the immune system does not attack it. Phospholipids • Has a hydrophilic (water loving head) • Hydrophobic (water fearing) Tail • Made up mostly of carbon (black)& Hydrogen (light blue) Phospholipid bi-layer • The cell membrane is made up of 2 layers of phospholipids. • The Hydrophilic heads face out. • The Hydrophobic tails face inward Other Membrane components Cholesterol makes the cell membrane more stiff and less permeable. Membrane Proteins function to: • Transport proteins – regulate the movement of water-soluble molecules through the cell membrane. • Receptor proteins –recognizes and binds to specific molecules. Often trigger some response by the cell such as endocytosis or cell division. • recognition proteins – identifies the cell as belonging to a specific species or organ. Helps immune system tell invading cells from cells belonging to the organism.