* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside the Eukaryotic Cell
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
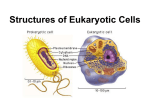
Only eukaryotic cells have A. DNA B. Membrane-bound organelles C. Ribosomes D. Cytoplasm Eukaryotic Cells Each organelle allows the cell to perform highly sophisticated and specialized functions Cytoskeleton Protein fibers found in eukaryotic cells Supports the cell like the bones support a body The cytoskeleton helps the cell move, keep its shape, and organize its parts. Types of cytoskeleton fibers Microfilaments Microtubules Intermediate fibers All of these are classified as protein fibers Microfilaments Contract and pull the cell to help it move and change shape Microtubules Hollow tubes that information molecules move through Intermediate Fibers Anchor organelles and enzymes to certain parts of the cell Eukaryotic DNA is packaged in the nucleus DNA along with some proteins must be kept separate from the cytoplasm Nucleus Surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope Nuclear envelope has pores which allow substances to pass in and out Nucleus Nucleolus is the region where ribosome parts are made Parts leave through the pores into the cytoplasm Ribosomes Can be “free” or “bound” Free float in the cytoplasm Bound are attached to organelles Both make proteins Microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate fibers are three kinds of cytoskeleton A. Protein fibers B. Membranes C. Organelles D. DNA What kind of cytoskeleton fibers could help a cell change shape to fit into a space? A. Microfilaments B. Microtubules C. Intermediate fibers D. Tubulin Fibers Which of the following is true of both DNA and some proteins? A. Made in the nucleus B. Made in ribosomes C. Must be kept separate from cytoplasm D. Must be kept separate from nucleus The double membrane surrounding the nucleus is called the A. Nucleolus B. Nuclear wall C. Ribosome D. Nuclear Envelope In a cell, proteins are made on the A. Mitochondria B. Ribosomes C. Nucleus D. Cell membrane Protein Processing Proteins have many purposes The endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus are organelles that prepare proteins for extracellular export Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Move proteins and other substances through cell Rough – Ribosomes are attached which make it appear “rough”. Part of ER that makes proteins Smooth - no attached ribosomes make lipids and break down toxic substances Golgi Apparatus Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for distribution Central Vacuole Found in many plant cells Stores water, ions, nutrients, and waste products Energy Production The energy for cellular functions is produced by chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria and chloroplasts Mitochondria Uses energy from organic compounds to make ATP Cells that require more energy may have more mitochondria Where are bound ribosomes located? A. Suspended in the cytosol B. Inside the nucleus C. Attached to membranes of another organelle D. Outside the cell membrane The organelle that moves proteins and other substances through the cell is the A. Endoplasmic reticulum B. Mitochondria C. Golgi apparatus D. Cytoplasm The organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins is the A. Endoplasmic reticulum B. Ribosome C. Lysosome D. Golgi apparatus Some plant cells have a large membrane-bound compartment in which water, waste products, and nutrients can be stored. This compartment is called the A. Mitochondria B. Chloroplast C. Golgi Apparatus D. Central Vacuole A cell that requires a lot of energy might contain a large number of A. Chromosomes B. Vacuoles C. Mitochondria D. Lysosomes The organelles associated with plant photosynthesis are the A. Mitochondria B. Chloroplasts C. Golgi apparatus D. Vacuoles What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? A. Absorption of light energy B. Presence in all cells C. Production of ATP D. Digestion of cell wastes