* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download U1L5Vocab
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
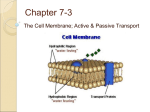
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Unit 1 Lesson 5 Vocabulary 1. Homeostasis: the maintenance of a constant state in a changing environment. (working to stay the same even though the environment is trying to change you) 2. Permeable: anything can pass through 3. Semi-permeable: allowing only some things to pass through 4. Passive transport: movement of particles across the cell membrane without using the cell’s energy 5. Concentration: the number of molecules of a substance in a specific volume (the number of molecules in a specific area). 6. Diffusion: movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration 7. Osmosis: diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane. Type of passive transport 8. Active transport: using the cell’s energy to move particles from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration (against a concentration gradient) 9. Endocytosis: process using the cell’s energy where a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell 10. Exocytosis: process using the cell’s energy where the cell releases a particle by enclosing it in a vesicle that then moves to the cell’s surface and fuses with the cell membrane Unit 1 Lesson 5 Vocabulary 1. Homeostasis: the maintenance of a constant state in a changing environment. (working to stay the same even though the environment is trying to change you) 2. Permeable: anything can pass through 3. Semi-permeable: allowing only some things to pass through 4. Passive transport: movement of particles across the cell membrane without using the cell’s energy 5. Concentration: the number of molecules of a substance in a specific volume (the number of molecules in a specific area). 6. Diffusion: movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration 7. Osmosis: diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane. Type of passive transport 8. Active transport: using the cell’s energy to move particles from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration (against a concentration gradient) 9. Endocytosis: process using the cell’s energy where a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell 10. Exocytosis: process using the cell’s energy where the cell releases a particle by enclosing it in a vesicle that then moves to the cell’s surface and fuses with the cell membrane Unit 1 Lesson 5 Vocabulary 1. Homeostasis: the maintenance of a constant state in a changing environment. (working to stay the same even though the environment is trying to change you) 2. Permeable: anything can pass through 3. Semi-permeable: allowing only some things to pass through 4. Passive transport: movement of particles across the cell membrane without using the cell’s energy 5. Concentration: the number of molecules of a substance in a specific volume (the number of molecules in a specific area). 6. Diffusion: movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration 7. Osmosis: diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane. Type of passive transport 8. Active transport: using the cell’s energy to move particles from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration (against a concentration gradient) 9. Endocytosis: process using the cell’s energy where a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell 10. Exocytosis: process using the cell’s energy where the cell releases a particle by enclosing it in a vesicle that then moves to the cell’s surface and fuses with the cell membrane