* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch07a
Mind-wandering wikipedia , lookup
Sex differences in cognition wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
False memory wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
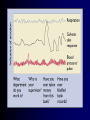
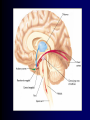
Memory • Memory: the storage, retention and recall of events, information and procedures. • The quality of a memory may vary – Interesting – Significant Ebbinghaus and Memory • Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve Ebbinghaus and Memory • What you recall depends on how you are tested – Recall: simple for the tester but difficult for the person being tested. (Essay Exams) – Cued recall: gives significant hints about the correct answer. (Fill-in-the-blank) – Recognition: Identify the correct item from a list. (Multiple-choice) The Information-Processing “Computer” • Sensory Memory • Short-Term Memory • Long-Term Memory The Information-Processing View of Memory • Capacities of Short and Long-Term Memory – This “magic range” of 7 +/- 2 bits is a wellreplicated finding regarding the capacity of short-term memory. – It can be expanded through techniques such as chunking, into larger, meaningful units. • Area code-Exchange-Number Information-Processing View • Working Memory – Working memory is a revised concept of short-term memory – Working memory is a system for processing or working with current information. • Working memory is conceptualized as having three major components. Three Components of W.M. • A phonological loop that stores and rehearses information • A visuospatial sketchpad: stores and manipulates visual and spatial information. • A central executive that governs shifts of attention. Good working memory is able to handle shifts between two or more tasks Information-Processing View • Other Memory Distinctions – Declarative: the ability to state a fact. – Procedural: is the memory of how to do something. – Long-term declarative memory is classified as either semantic (dealing with principles of knowledge) or episodic (containing events and details of life history.) Memory Improvement • To improve memory, one must improve the strategies used to originally store the material. The Influence of Emotional Arousal • It is well understood that the greater the emotional arousal associated with an event, the greater the likelihood that the event will be remembered. • This does not mean that all components of the memory will be accurate! Emotional Arousal • During stressful or emotional events, the sympathetic nervous system works to boost production of the hormones cortisol and adrenaline. • This is usually accompanied by increase stimulation of the amygdala. • You are more likely to remember joyous or traumatic events than any other type of event. Meaningful Storage and Levels of Processing • The levels-of-processing principle – The levels-of-processing principle states that the ease with which we can retrieve a memory depends on the number and types of associations that we form with that memory Levels of Processing • Superficial processing – simply repeating the material that you are trying to memorize. • Deeper processing – think about each item or parts of the material individually. • Still deeper processing – note the associations between the items or parts of the material. Timing of Study Sessions • The Serial-Order Effect – The serial-order effect states that we tend to remember the beginning and end of a list better than the middle. • The primacy effect is the tendency to remember the beginning. Low proactive interference. • The recency effect is the tendency to remember the end. Low retroactive interference. Special Coding Strategies • Retrieval Cues – The encoding specificity principle states that the associations formed at the time of learning are typically the most effective retrieval cues. – State-dependent memory is our tendency to remember something better if your physical condition is the same at the time of recall as it was at the time of learning. Special Coding Strategies • Mnemonic Devices – The method of loci involves memorizing a series of places. Using a vivid image, you associate each of these locations with something you want to remember. – The peg method involves memorizing a list of objects (“pegs”) and forming mental images to link the information that you wish to memorize using these pegs. Improving Our Memory • We refer to our memories as “stored” and “retrieved” as if they were items on a shelf in a warehouse. But this analogy is only partially useful. • The more you know about a topic, the more interested you are in it, the easier it is to establish and retain new information related to the topic. Emotion • Emotion – Though emotions comprise a crucial part of our individual and social experiences, they are elusive concepts. How can we difficult to define and measure them? Emotions & Decision-Making • It makes intuitive sense that good decision-making would require some great degree of emotional control • This in fact is not entirely true. Only extreme emotions interfere with decisionmaking. • Some degree of emotionality appears to be necessary for good decision-making. Emotions & Decision-Making • A fear of fire would make you flee a burning building. • The same fear keeps a fire fighter alert and vigilant while entering a burning building • Is the emotion (fear) a good thing in these two situations? • Would you want to work with a “fearless” firefighter? Emotions and Decision-Making • Case Studies: – Phineas Gage – Antonio Damasio’s “Elliot” – V.S. Ramachandrin and Capgras’delusion Emotions and Decision-Making • The ability to imagine the feeling that we would have pursuing each option presented to us is a big part of good decision-making capability. “Emotions are inseparable from the idea of good and evil.” -- Antonio Damasio Emotional Intelligence • Emotional intelligence is defined as the ability to perceive, imagine and understand emotions and to use that information in decision-making. Excitement and Physiological Arousal • The Autonomic Nervous System – The autonomic nervous system is the division that controls the functioning of the internal organs. – The ANS has two subdivisions, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The Autonomic Nervous System • The Two Divisions of the ANS – Both systems are active, and the shifting between the two systems helps to keep the body in homeostasis. – Emergencies activate the sympathetic nervous system and energy is used – The parasympathetic nervous system takes over in peaceful situations and energy is conserved The Autonomic Nervous System • We generally cannot directly control autonomic responses, but we can influence them – Parasympathetic • Breathing exercises • Relaxation – Sympathetic • Running, shouting Autonomic Nervous System • The Opponent Process Principle – The experience of any emotion can be thought of as a “pull” away from a emotionless center – Intense emotions will be followed by a “rebound.” • Terror followed by immense relief and joy – Clinical implications: Bipolar Disorders Autonomic Nervous System • The Sympathetic Nervous System and Lie Detection – Throughout history, humans have been determined to find a reliable test to determine whether a person is telling the truth or is lying. – One of the most frequently used methods involves the use of a polygraph or “lie detector.” Autonomic Nervous System Lie Detection • Polygraph test procedure does identify a large number of guilty people, it also misses many and falsely identifies some innocent people as guilty. – The guilty-knowledge test is a variant of the standard test that produces more accurate results. Emotion and Perceived Arousal • Which comes first, the psychological experience of emotion or the physiological arousal? • Common sense dictates: – You feels sad and then you cry – You feel happy and then you laugh Emotion and Perceived Arousal • • Two nineteenth century psychologists proposed different theories of emotion and physiology James-Lange theory 1. You process the available information 2. Your body responds 3. Your emotions are determined by your body’s response Emotion and Perceived Arousal • Schachter and Singer’s Theory – The physiological state is not the same thing is the emotion. – The physiological responses does not determine the emotion, but will determine its intensity The Range of Emotions • Understanding Facial Expressions – Researchers have found a large amount of evidence that there is indeed a set of basic emotions. – Many facial expressions including smiling, frowning, laughing, and crying occur throughout the world and are even found in children who were born deaf and blind. The Range of Emotions • Understanding Facial Expressions – Some of our facial expressions develop in the absence of opportunities to observe and imitate others (blind individuals). – Evidence of basic emotions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Happiness Sadness Fear Disgust Anger Surprise. Biological Basis of Emotions • There is evidence linking the emotions of fear or anxiety to the amygdala. – When the amygdala is damaged, a person’s ability to experience these feelings may be impaired. Biological Basis of Emotions • Damage to the amygdala also diminishes the ability to recognize the signs of these feelings in other people. • Also impairment in the ability to recognize anger, disgust and surprise The amygdala may be specialized to process information relative to several kinds of emotions Disconnecting Perception and Emotion • Prosopagnosia Feeling Fact – Factual information is not available, but the emotional information is – “I can’t recognize that woman, but I feel good when I see her” Disconnecting Perception and Emotion • Capgras Delusion Feeling Fact – Factual information is available, but there is no emotional content – “That woman looks like my mother, but is really an imposter” Emotions • The debates described in this module may not strike you as terribly important, but they are part of larger issue of great importance to the science of psychology. • Human behavior seems to be in large part influenced by emotions.