* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download State of Climate Change and Water Modeling in Bangladesh
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
North Report wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
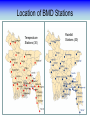
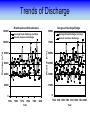
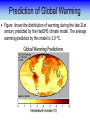
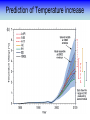
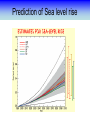
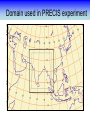
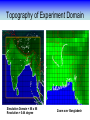
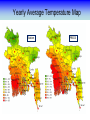
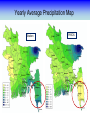
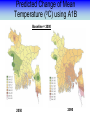
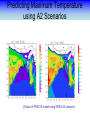
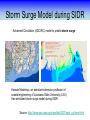
Training Program on Water Security and Climate Change State of Climate Change and Water Modeling in Bangladesh A.K.M. Saiful Islam Associate Professor, IWFM Coordinator, Climate Change Study Cell Bangladesh University of Engineer and Technology (BUET) Presentation Outline • Overview of the Trend of temperature of Bangladesh and Climate System • Modeling of Climate Change • General Circulation Model (GCM) • IPCC SRES Scenarios • Climate Change Scenarios • Regional Climate Model (RCM) • Climatic Modeling at BUET • Storm Surge and Salinity modeling due to SLR Location of BMD Stations Temperature Stations (30) Rainfall Stations (30) Trends of Temperature of Bangladesh (1947-2007) Max. Temp. = 0.63 0C/100 year Min. Temp. = 1.37 0C/100 year 2008 2005 2002 1999 1996 1993 1990 1987 1984 1981 1978 1975 2008 2005 2002 1999 1996 1993 1990 1987 1984 1981 1978 1975 1972 1969 1966 20 1963 29.4 1960 20.2 1957 20.4 29.6 1954 20.6 1951 30 29.8 1966 20.8 1963 21 30.2 1960 21.2 30.4 1957 30.6 1954 21.4 1951 30.8 1948 21.6 1948 y = 0.0137x - 6.0268 21.8 31 1972 y = 0.0063x + 17.855 31.2 Trends of Minimum Temperature 22 1969 Trends of Maximum Temperature 31.4 Trends of Discharge Brahmaputra at Bahadurabad Ganges at Hardinge Bridge 120000 90000 Average flood discharge (Jul-Sep) Annual maximum discharge Average flood discharge (Jul-Sep) Annual maximum discharge 75000 Discharge (m3 /s) Discharge (m3 /s) 100000 80000 60000 40000 60000 45000 30000 20000 15000 0 0 1954 1964 1974 1984 Year 1994 2004 1934 1944 1954 1964 1974 1984 1994 2004 Year Spatial Distribution of Trends of Temperature (1947-2007) Maximum Temperature Maximum increase: 0.0581 at Shitakunda Minimum increase: -0.026 at Rangpur Minimum Temperature Maximum increase: 0.0404 at Bogra Minimum increase: -0.023 at Tangail Climate Models • Climate models are computer-based simulations that use mathematical formulas to re-create the chemical and physical processes that drive Earth’s climate. To “run” a model, scientists divide the planet into a 3-dimensional grid, apply the basic equations, and evaluate the results. • Atmospheric models calculate winds, heat transfer, radiation, relative humidity, and surface hydrology within each grid and evaluate interactions with neighboring points. Climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. General Circulation Model (GCM) • General Circulation Models (GCMs) are a class of computerdriven models for weather forecasting, understanding climate and projecting climate change, where they are commonly called Global Climate Models. • Three dimensional GCM's discretise the equations for fluid motion and energy transfer and integrate these forward in time. They also contain parameterizations for processes such as convection - that occur on scales too small to be resolved directly. • Atmospheric GCMs (AGCMs) model the atmosphere and impose sea surface temperatures. Coupled atmosphereocean GCMs (AOGCMs, e.g. HadCM3, EdGCM, GFDL CM2.X, ARPEGE-Climate) combine the two models. GCM typical horizontal resolution of between 250 and 600 km, 10 to 20 vertical layers in the atmosphere and sometimes as many as 30 layers in the oceans. Heart of Climate Model Conservation of momentum Conservation of mass Conservation of energy Complexity of GCM Hardware Behind the Climate Model • Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (SRES) • The Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (SRES) was a report prepared by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) for the Third Assessment Report (TAR) in 2001, on future emission scenarios to be used for driving global circulation models to develop climate change scenarios. • It was used to replace the IS92 scenarios used for the IPCC Second Assessment Report of 1995. The SRES Scenarios were also used for the Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) in 2007. SERS Emission Scenarios • A1 - a future world of very rapid economic growth, global population that peaks in mid-century and declines thereafter, and the rapid introduction of new and more efficient technologies. Three sub groups: fossil intensive (A1FI), non-fossil energy sources (A1T), or a balance across all sources (A1B). • A2 - A very heterogeneous world. The underlying theme is that of strengthening regional cultural identities, with an emphasis on family values and local traditions, high population growth, and less concern for rapid economic development. • B1 - a convergent world with the same global population, that peaks in mid-century and declines thereafter, as in the A1 storyline. • B2 - a world in which the emphasis is on local solutions to economic, social and environmental sustainability. GCM output described in the 2007 IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (SRES scenarios), multilayer mean Models Variables BCC:CM1 BCCR:BCM2 CCCMA:CGCM3_1-T47 CCCMA:CGCM3_1-T63 CNRM:CM3 CONS:ECHO-G CSIRO:MK3 GFDL:CM2 GFDL:CM2_1 INM:CM3 IPSL:CM4 LASG:FGOALS-G1_0 MPIM:ECHAM5 MRI:CGCM2_3_2 NASA:GISS-AOM NASA:GISS-EH NASA:GISS-ER NCAR:CCSM3 NCAR:PCM NIES:MIROC3_2-HI NIES:MIROC3_2-MED UKMO:HADCM3 UKMO:HADGEM1 specific humidity precipitation flux air pressure at sea level net upward shortwave flux in air air temperature air temperature daily max air temperature daily min eastward wind northward wind Prediction of Global Warming • Figure shows the distribution of warming during the late 21st century predicted by the HadCM3 climate model. The average warming predicted by this model is 3.0 °C. Prediction of Temperature increase Observed Ice melting http://www.worldwithoutwinter.com/melting%20ice%20caps.jpg • Images gathered from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program of NASA show the minimum Arctic sea ice concentration 1979 (left) and 2003 (right). 1979 2003 Predicted Arctic sea Ice Arctic Sea Ice in 2000 Arctic Sea Ice in 2040 Results from community climate system models Prediction of Sea level rise Regional details of Climate Change Regional Climate modeling • An RCM is a tool to add small-scale detailed information of future climate change to the large-scale projections of a GCM. RCMs are full climate models and as such are physically based and represent most or all of the processes, interactions and feedbacks between the climate system components that are represented in GCMs. • They take coarse resolution information from a GCM and then develop temporally and spatially fine-scale information consistent with this using their higher resolution representation of the climate system. • The typical resolution of an RCM is about 50 km in the horizontal and GCMs are typically 500~300 km Regional Climate change modeling in Bangladesh • PRECIS regional climate modeling is now running in Climate change study cell at IWFM,BUET. • Uses LBC data from GCM (e.g. HadCM3). • LBC data available for baseline, A2, B2, A1B scenarios up to 2100. • Predictions for every hour. Needs more than 100 GB free space. Domain used in PRECIS experiment Topography of Experiment Domain Simulation Domain = 88 x 88 Resolution = 0.44 degree Zoom over Bangladesh Yearly Average Temperature Yearly Average Temperature Map Station PRECIS Yearly Average Precipitation of Bangladesh Yearly Average Precipitation Map Station PRECIS Predicted Change of Mean Temperature (0C) using A1B Baseline = 2000 2050 2090 Change of Mean Rainfall (mm/d) using A1B Scenarios Baseline = 2000 2050 2090 Predicting Maximum Temperature using A2 Scenarios [Output of PRECIS model using SRES A2 scenario] Change of Mean Rainfall (mm/d) using A1B Scenarios Baseline = 2000 2050 2090 Change of mean climatic variables of Bangladesh using A1B Scenarios Temperate (0C) Rainfall (mm/d) High-resolution Regional Climate Change Information for Bangladesh to inform Impacts assessments, Vulnerability indicators and Adaptation policies Experiment ID adqcm erain ncepb addfa addfb addfc addja addje addjf addjd aenwh echfa echja echjd echvc Description of the Simulation ERA40:Reanalysis ERA-Interim: Reanalysis NCEP_R2:Reanalysis HadAM3P:Baseline#1 HadAM3P:Baseline#2 HadAM3P:Baseline#3 HadAM3P:SRES_A2#1 HadAM3P:SRES_A2#2 HadAM3P:SRES_A2#3 HadAM3P:SRES_B2 HadCM3Q0:SRES_A1B ECHAM4:Baseline ECHAM4:SRES_A2 ECHAM4:SRES_B2 ECHAM5:SRES_A1B Time Frame 1957-2001 1989-2009 1979-2004 1960-1990 1960-1990 1960-1990 2070-2100 2070-2100 2070-2100 2070-2100 1949-2099 1960-1990 2069-2100 2069-2100 1950-2100 Length( years) 40 20 25 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 150 30 30 30 150 Storm Surge Model during SIDR Advanced Circulation (ADCIRC) model to predict storm surge Hassan Mashriqui, an assistant extension professor of coastal engineering of Louisiana State University (LSU) Has simulated storm surge model during SIDR Source: http://www.oar.noaa.gov/spotlite/2007/spot_cyclone.html 2D Hydrodynamic Modeling for Salt water Intrusion IWM studied “Impact of Sea level Rise on Coastal Rivers of Bangladesh” Five ppt line for different sea level rise in dry season What will happen to Artic Polar Bears ? Antarctic Penguins are watching… The Sundarbans ..Mangrove forest? Thank you