* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An informatics approach to analyzing the incidentalome
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Exome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
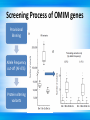
An informatics approach to analyzing the incidentalome J.Berg et al. Genetics in Medicine Presented by Li Changjian Concept • Incidentalome: Incidental findings of genetic variants unrelated to presenting symptoms during the genetic diagnosis using whole genome sequencing (WGS) Challenge on Incidentalome • Reducing cost in WGS makes it available for genetic diagnosis • Vast volume of genomic findings with dubious clinical value is generated, overwhelming of information to physicians and patients • A good screening/sifting method for the genetic data is needed Binning System • Categories the genetic data Subjects & Methods • Focus: Monogenic Disorders • OMIM genes for provisional binning (12786 genes) • 80 genome sequences used as test sequences, 19 from paints and 61 from presumably healthy individuals • Database: PostgreSQL 8.4.3, Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) and NCBI build 37 • Python script used to determine the zygosity Screening Process of OMIM genes Provisional Binning Allele Frequency cut-off (AF<5%) Protein-altering variants Further Screening • Presence in a binned gene • <5% AF (Low Probability Mendelian Disorder) • Either being annotated as diseasing-causing mutation (DM) in HGMD or predicted to be truncating • Analyze zygosity to assign heterozygous variants in recessive genes to determine carrier status • Finally, manual review to assess evidence of pathogenicity, reclassify the binning Summarized Results Screening processes of the informatics algorithm Significant reduction the number of binned genes Example Results High specificity for bin 1 and bin 2c variants Sensitivity and Specificity • Excluding synonymous variants, noncoding variants scarifies the sensitivity for higher specificity • No gold standard to definitively estimate the specificity and sensitivity • The sensitivity and specificity ties to quality of clinical database due to the data querying and predictive algorithms. Comparison with other reports • Substantial difference resulted by different assumptions (ignoring SNPs variants) • Stringent requirements on genes having clinical utility raise the thresholds results four orders less (0-2 variants versus 2000 variants by Cassa et al.) returned variants in bin 1. • The specificity of current binning system is higher Limitations • Only monogenic diseases is studied in this paper • Specificity and Sensitivity needs quantitative estimation • Number of variants in manual review process in the last step is still large (~100s) Future directions • Extend the method the multifactorial diesease • Subcategorize Bin 2b into disease groups • Establish more granular criteria to determine the novel variants selected for review • To better understand the penetrance of a certain variants • To improve and maintain clinical-grade database of known variants Conclusion • Proof of concept of an framework to organizing the incidental findings during WGS to reduce the number of variants to be hand curated to a manageable number.