* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drosophila - mccombsscience
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
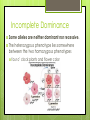
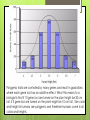
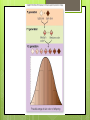
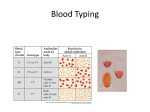
Gene Linkage and Patterns of Inheritance Gene Linkage and Gene Maps Exception to Mendel’s rule of independent assortment Thomas Hunt Morgan experimented with Drosophila (the common house fly) Reddish-orange eyes and miniature wings almost always inherited together Observed this trend in many genes Grouped all the fly’s genes into four linkage groups Drosophila has four linkage groups and four pairs of chromosomes Conclusions 1. 2. Each chromosome is actually a group of linked genes Mendel’s law of independent assortment still true It is the chromosomes that assort independently, not individual genes Gene Mapping The relative locations of genes on a chromosome can be determined by using the frequency of crossing-over between genes Patterns of Inheritance Exceptions to Mendel’s principles Most genes have more than two alleles Many important traits are controlled by more than one gene Incomplete Dominance Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. The heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes four o’ clock plants and flower color Codominance The phenotypes produced by both alleles are expressed. Chicken feathers- heterozygous= “erminette”- speckled with black and white feathers Blood type- A and B are codominant Multiple Alleles A gene with more than tw0 alleles Rabbit coat color An individual still only has two copies of each gene A single gene with at least four different alleles Blood type A, B, and O Polygenic Traits Traits that are produced by the interaction of several genes Skin color, height Show a normal distribution (bell-shaped curve) Polygenic traits are controlled by many genes and result in gradations where each gene loci has an additive effect. What this means to a biologist is that if 10 gene loci are turned on the plant might be 20 cm tall. If 5 gene loci are turned on the plant might be 10 cm tall. Skin color and height in humans are polygenic and therefore humans come in all colors and heights. Sex-Linked Inheritance The genes located on the X and Y chromosome show a pattern of inheritance called sex-linkage Genes found on the Y chromosome are found only in males and are passed directly from father to son Genes on the X chromosome are found in both sexes, but the fact that men have just one X chromosome leads to some interesting consequences Sex-linkage: colorblindness Humans have 3 genes responsible for color vision, all on the X chromosome In males, a defective allele for any of these genes results in colorblindness Red-green colorblindness occurs in 1 in 12 males 1 in 200 in females Colorblindness must be present in both alleles to be expressed in females Genes and the Environment The phenotype of an organism is only partly determined by its genotype Western white butterfly Western whites hatching in summer have different color patterns on wings than those hatching in spring More pigment in butterflies of the shorter days of spring Spring months are cooler; greater pigmentation helps them reach the body temp needed for flight