* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2b.-Citric-Acid-Cycle
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
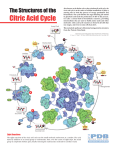
(7) Cellular Respiration (A) Role of ATP & Phosphorylation (B) The metabolic pathway of respiration: Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle Cellular Respiration (C) The metabolic pathway of respiration: electron transport chain & ATP synthesis (E) Regulation of pathways through feedback inhibition (D) Substrates for Respiration Cellular Respiration (b) • Describe the process of the Citric Acid Cycle –Using the terms coenzyme, regeneration, oxaloacetate, FAD Stage 2 Citric Acid Cycle (occurs only if oxygen is present) Pyruvate NAD NADH CO2 Acetyl group Coenzyme A Acetyl Coenzyme A citrate 2 CO2 oxaloacetate ADP ATP 3FAD 3FADH2 3NAD 3NADH Notice the 2 is present on the FAD but not the NAD 1 • Pyruvate is broken down to an acetyl group that combines with coenzyme A to be transferred to the 2 citric acid cycle as acetyl coenzyme A. 3 • Acetyl (coenzyme A) combines with oxaloacetate to 4 form citrate followed by the enzyme mediated steps of the cycle. 5 • This cycle results in the generation of ATP in one of the steps, the release of carbon 6dioxide in 2 of the steps and the regeneration of oxaloacetate in the 7 matrix of the mitochondria. 8 • In three steps in the cycle, the dehydrogenase enzyme removes H+ ions along with high energy 9 electrons. Both become bound to NAD to form 10 NADH. 10 • A similar step also occurs, but the coenzyme is FAD. Checklist Name of stage Location Starting molecule(s) Intermediate molecule(s) Final molecule(s) ATP Carbon dioxide Hydrogen Oxygen Any other points? Extra info that will help you understand (but you will not be examined on this) Number of carbons in each molecule: • • • • • GLUCOSE PYRUVATE ACETYL CO A OXALOACETATE CITRATE 6 3 2 4 6 (gets broken down) (gets broken down more!) (2+4=6) Investigating the activity of dehydrogenase enzyme in yeast • Yeast is a fungus and a living organism. All living organisms can respire. Like us, it also contains the enzyme dehydrogenase which controls the release of hydrogen during respiration. • To show the release of hydrogen during respiration a blue dye called resazurin is used. The dye changes colour upon becoming reduced (gaining hydrogen). Blue (Not reduced) Pink (partially reduced) Colourless (reduced) Aim: To investigate… Method: Results: Test tube A B C Colour change of resazurin dye • Conclusion: – What test tube changed colour the fastest? – Describe the process which occurred in tube A: • ______ enzymes present in the _____ have acted on the substrate _____ and oxidised it. This rapid release of _____has reduced the resazurin dye and caused it to change colour. – Explain why the reaction in test tube B was slower than test tube A. • Test tube was slower than A because no glucose was added. The dehydrogenase enzymes could act upon the little respiratory substrate already present in the yeast. – Explain why test tube C remained unchanged. • Test tube C remained unchanged since boiled yeast was added. Boiling the yeast destroys the cells and denatures the dehydrogenase enzymes. Cellular Respiration (b) • Describe the process of the Citric Acid Cycle –Using the terms coenzyme, regeneration, oxaloacetate, FAD
















![NEC313N, ACETYL COENZYME A, [ACETYL-1- C]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003392842_1-f84d6512b3156ee480c7453e33ca6834-150x150.png)