* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life is Cellular!
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
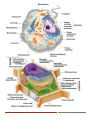
Life is Cellular! Biology/Hervey Life is Cellular! TEKS (4) Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells. The student is expected to: Materials - Warm Up- Concept map Quiz - Cell picture print out - Microscopes with slides of cells - Toothpick lab (A) compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Vocabulary Learning Targets/Objectives After the lesson students will be able to” Discuss the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Identify eukaryotic cell organelles Analyze plant versus animal cell structures and their functions Activities Warm-Up- Students will work on cell structures and function concept map quietly and independently. Warm is a review over last nights reading for daily quiz. 7min Quiz over last nights reading (5 questions/1min) FOR A GRADE 5-10 mins -In 1665, Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at a thin slice of cork, a plant material. -Cells are the basic unit of life…(Smallest functional unit) -Similar to a car, living organisms are the cars but all the parts (steering wheel, brakes, engine, etc) all work together to allow the car to be. Each one is dependent upon the other. The cell Theory: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. 20min Terms to know: Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Nucleus Cell Membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Mitochondria vs. Chloroplast Cytoplasm Other Resources - BrainPOPs - Exit quiz - Experience Biology - Khan Academy - Gizmos https://prezi.com/gpohegw-ybbv/biologychapter-7-section-1-life-is-cellular/ https://prezi.com/dkm2dcvp_7jd/biologychapter-7-section-2-eukaryotic-cellstructures/ Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes - cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes all cells are surrounded by a barrier called cell membrane and contain DNA Cells are classified into 2 groups based on whether or not they have a nucleus. The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA. It looks like a dark ball under a microscope. The nucleus controls many of the cell's activities. Eukaryotes= with nucleus Prokaryotes= no nucleus SHOW PICTURE Life is Cellular! Biology/Hervey In groups at table: list characteristics of prokary. vs. eukaryo. Plant vs. Animal (divide up, then have students write them down on sticky notes and place them on the cell pictures on the wall. Include an example of each.) [use book] 15 min Other Notes: Prokaryotic cells have genetic material that is not contained in a nucleus. - Prokaryotes do not have membrane-bound organelles. - Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells. - All prokaryotes are Bacteria. 20min Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell. - Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells generally contain dozens of structures and internal membranes. Many eukaryotic cells are highly specialized. Plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes. Components of a Cell (Organelles) Nucleus- control center, contains DNA Cell Membrane-out layer of the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum – packages proteins Ribosomes- Protein synthesis Golgi Apparatus – modifies proteins and packages it Lysosomes- contains digestive enzymes, break down bacteria Mitochondria vs. Chloroplast – energy sythesis Cytoplasm – contains most of organelles Centriole vacuole (plants)- stores water Classwork Finish classwork packet 7.1 - 7.2 could have been completed as homework to study for quiz today. If so, student receives technology time remaining 15mins of class Evaluation/Assesment Students will complete an exit quiz a BrainPOP quiz on technology. Exit 7min WARM UP/CONCEPT MAP http://www.biologyalive.com/life/classes/biology/documents/Unit%207/chapter07/Biology%207%20GO.pdf Life is Cellular! Biology/Hervey