* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
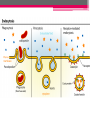
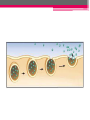
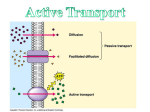
Active Transport SBI 4U Ms.Zafar October 24th, 2012 Review • Diffusion • Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion • Protein carrier molecules, located in the cell membrane, can aid in passive transport Facilitated Diffusion, continued … • Protein carriers speed up the movement of molecules already moving across the cell membrane • Example: glucose diffuses into red blood cells hundreds of times faster than other sugar molecules that have similar properties, why? specialized carrier proteins Active Transport • When a cell uses its own energy to move materials from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration active transport Without active transport … • Your kidneys would fail to reabsorb needed materials • Your muscles would not contract • Your nerves would not carry impulses Endocytosis & Exocytosis • How do cells absorb larger molecules? Expenditure of energy is required • Endocytosis process of ingesting materials • Exocytosis process of transporting materials to outside environment Process of Endocytosis 1. 2. 3. Membrane folds around materials outside the cell Ingested particle is trapped within a vacuole inside the cytoplasm Often lysosomes are used to digest the molecules absorbed by endocytosis Endocytosis, continued … • Pinocytosis & Phagocytosis • Pinocytosis: cells take up dissolved molecules by engulfing small volumes of the external solution. Ex: small intestine and fat droplets • Phagocytosis: process by which cells engulf solid particles. Ex: white blood cells and microbes • Cellular drinking vs. cellular eating Exocytosis • Process by which large molecules held within the cell are transported to the external environment • Waste materials are often released this way • Useful materials, like transmitter chemicals emitted from nerve cells are also released by exocytosis Process of Exocytosis 1. Golgi apparatus holds the secretions inside fluid-filled membranes 2. Small vesicles break off and move toward the cell membrane 3. The vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and the materials is released into the external environment