* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - mrhebert.org
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
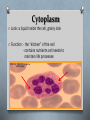
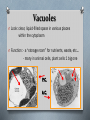
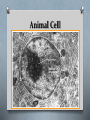
Cells The Basic Units of Life Cell Structures Cell Membrane O Look: a thin line that surrounds the whole cell O Function: - barrier between inside/outside and what comes in/out - helps with shape/form Cell Wall O Look: a rigid, frame-like covering that surrounds the cells O Function: - helps regulate pressure in the cell (too much water in or out) - also protects the cell - only in plant cells Cytoplasm O Look: a liquid inside the cell, grainy look O Function: - the “kitchen” of the cell - contains nutrients cell needs to maintain life processes Nucleus O Look: a fairly large, dark, circular structure usually near the center of the cell O Function: - a “command center” - directs all cellular activity (i.e.: growth, movement) Vacuoles O Look: clear, liquid-filled space in various places within the cytoplasm O Function: - a “storage room” for nutrients, waste, etc… - many in animal cells, plant cells 1 big one P.C. A.C. Chloroplasts O Look: medium sized, green circular shaped structures, typically around edges of cell O Function: - solar panel of the cell & found on green parts (i.e.: leaves) - perform photosynthesis & only plant cells Animal Cell Plant Cell Organelles O Most cellular life cannot be seen with a light microscope O Problem solved with electron microscope Organelles O Organelles: specialized structures that carry out specific functions O Cells work just like mini factories in that they have specialized areas to accomplish specific tasks Organelles O Mitochondria: - “powerhouse” of the cell - chemical reactions occur here converting energy cell receives to form it can use Uni vs. Multi Cellular O Smallest known organism is the mycoplasma which is magnified 18000x to be viewed O This is a single cell organism (as are most bacteria) Uni vs. Multi Cellular O Largest known animal is the blue whale, it can be 30m long O It is a multicellular organism (as most plants/ animals are) UniCellular O Not all unicellular organisms are simple O See: Diatoms Amoeba O Common unicellular organism O Lives in water O Moves using tiny foot-like projections (pseudopods) O Uses them to eat too - engulfs food creating a vacuole then digests it into cytoplasm Paramecium O Another Common unicellular organism O This has tiny hairs all around it O Called cilia O They use it to move (like tiny oars) and to eat (sweeps food down into oral grooves where eaten) Substance Movement O Every second of every day your cells are moving things (waste, energy, nutrient, etc…) O This is vital for survival O Cells have a structure that permits vital exchange of substances cell membrane O Process is typically via diffusion Diffusion & Osmosis O Diffusion is key for plant roots O Moving and distributing evenly from areas of higher concentrations to lower concentration Diffusion O So what is it? O High Concentration to Low Concentration O An “evening out” process O Occurs until concentrations are the same everywhere O How? O Selectively permeable membrane O That is to say it allows certain things in (i.e.: oxygen) while holding what it needs in (i.e.: no cytoplasm leaking out) O For example: mitochondria need oxygen to function and diffuses into the cells as needed because the concentration is higher outside of the cell compared to inside Osmosis O Is essentially the same as diffusion but speaking specifically about water in cells O Diffusion of water particles through a selectively permeable membrane O Water from higher concentration to lower concentration O Why? O Water in cells need to stay relatively consistent for proper cell health and function Cells Reproduce O Unicellular organisms grow and develop O Differences? O When they reach their max they divide into two identical organisms O This is how your cells reproduce as well O It is how your body replaces the roughly 50000 skin cells it loses each day or repairs skin when you get scraped or cut Specialized Cells O Our bodies are made up of trillions of cells … many are specialized O Example: O Red blood cells carry oxygen, lose nucleus so they cannot self-reproduce when they mature and are pliable to fit small spaces O To reproduce they need other organs/tissues in the body O This case blood needs marrow (found in most bones) to make new cells Cell Categories Connective Tissue Nervous Tissue Epithelial Tissue Muscle Tissue Plant Cell Categories O Plants are similar in that they have 3 cell categories O 1) Photosynthesis/Storage O 2) Protective O 3) Transport O No organ systems exist in plants though however they need the substances produces/provided by the other cell categories to survive O Good way to identify them? Look at leaf, stem and root cells So ..! O Here is a question to see if you were paying attention! O Is a red blood cell more specialized than an amoeba or is it the other way around? O Discuss… Goodbye Topic 2