* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Stage 3 biology lesson plan - plant and animal cells
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
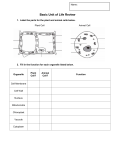
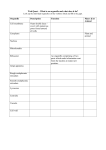
Key Words Cell, Tissue, Organ, System, Organism, Organelle, Cell membrane, Cell wall, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Chloroplast, Chlorophyll, Mitochondria/Mitochondrion, Specialised Activities 1. Get students to name different systems within the human body (e.g., digestive system, reproductive system, etc.). Get students to name particular organs within a certain system (for example, the small intestine). Explain how an organ is made up of different types of tissues, which are made up of different types of cells (see the image below). 2. Show students unlabelled diagrams of a plant and animal cells (shown below). © Education Umbrella, 2014 1 Provide students with labels and a brief description of the functions for each organelle. Students should use these descriptions as 'clues' to help them match the label to the correct organelle on each diagram. Descriptions are as follows: Cell Membrane- thin layer around cells that act as a 'barrier' - controls what substances go into and out of cells Mitochondria- the 'powerhouses' of cells - energy is generated here Nucleus- control centre for cells - where genetic information is stored Cytoplasm- a jelly-like substance within the cell where chemical reactions occur Cell Wall- provides support for cells and helps them maintain their rigid structure Chloroplast- small green structures where photosynthesis occurs Chlorophyll- contained within the chloroplast Vacuole- contains cell sap and keeps the cell firm 3. Get students to look at onion cells and cheek cells under a light microscope and try to identify the cell membrane, nucleus, vacuole and cell wall. Working Scientifically • Show students the process of carefully removing the thin layer of cells from the onion. © Education Umbrella, 2014 2 • Explain the importance of safety when taking cheek cell samples. (For example, cotton buds used to obtain cheek cells should not be reused.) • Show students how to adjust the magnification of a light microscope and how to get an image into focus. 4. Show students images of specialised cells and discuss adaptations that make them suited to their function (examples below). Questions a) What is the purpose of flagellum (tail) of a sperm cell? b) The shape of the root hair cell means it has a larger surface area compared to a rectangular cell of the same shape - why is a larger surface area advantageous for this type of cell? c) The nucleus of a white blood cell is 'multi-lobed,' allowing the cell to change shape more easily. Why this is important for a white blood cell? © Education Umbrella, 2014 3