* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity (1
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
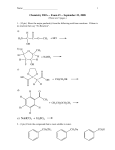
CHE 175 Spring, 2002 QUIZ 3 Name___________________________ ID (SSN)________________________ Instructor_______________________ SHORT ANSWER (10 pts each) 1. Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity (1 = most acidic à 5 = least acidic): O O O O O H N O O 2. Show the enol tautomer of 1,3,5-cyclohexatrione. Would you expect this compound to exist predominantly in the keto or enol form? O O O 3. Show the major product that's formed from each of the reaction sequences shown below with cyclohexanone. 1. Me2NH 2. CH3CH2I O 1. LDA, -78 °C 2. CH3CH2I 3. H2O, H+ 4. Show a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed α-bromination of acetone. 5. Show how you would carry out the following synthesis. O O MULTIPLE CHOICE (10 pts each) 6. What is the carbon nucleophile that attacks molecular bromine in the acid-catalyzed α-bromination of a ketone? (a) an enolate (b) a carbocation (c) an acetylide (d) an enol 7. The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction involves: (a) the α-bromination of carboxylic acids (b) the α-bromination of ketones (c) the bromination of alcohols (d) none of the above O (a) O H (b) H O H (c) H3C H3C (d) all of these CH 3 8. Which of the following compounds does NOT have an α-hydrogen? 9. Which of the following is a β-ketoester? O OH (a) O (b) O OEt O O O (c) (d) O 10. What is the major product of the following reaction? O 1. LDA, -78 °C 2. CH3 I, -78 °C O (a) O (b) O OH (c) (d) **Bonus (+5 pts): Explain what "LDA" is, how to make it, and what it's used for. O O