* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STUDY GUIDE Cells/Membrane Transport Cell Organelles What`s
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
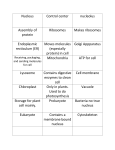
STUDY GUIDE Cells/Membrane Transport Cell Organelles ● What’s the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Prokaryote = no nucleus Eukaryote = nucleus ● What’s an example of a prokaryote? What’s a eukaryote? Prokaryote = bacteria Eukaryote = plants and animals ● What are 3 things found inside the nucleus? Chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins), chromosomes, nucleolus ● How are plant cells different than animal cells? Cell wall, chloroplasts, 1 large vacuole ● What is the function of the following organelles: ○ cell membrane support, protection, transport molecules in and out of cell ○ cell wall support, shape, protection in PLANT and BACTERIA cells, cellulose ○ nucleus holds genetic information (chromatin) ○ nucleolus makes ribosomes ○ smooth ER makes lipids ○ rough ER makes proteins (because of the ribosomes on the rough ER) ○ ribosome makes proteins ○ golgi apparatus packages and ships proteins to final destination ○ lysosome digests material (“food” and dead organelles) ○ vacuole stores water, salt, proteins ○ chloroplast goes through photosynthesis ○ mitochondria provides energy (ATP) ○ cytoskeleton helps move cell and cell organelles ○ cytoplasm liquid inside cell, mainly water Membrane Transport ● Draw and label the cell membrane below using the words: ○ phospholipid, protein, hydrophobic, hydrophilic, polar, nonpolar ● What’s the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic? Hydrophobic: something that doesn’t get along with water (nonpolar) Hydrophilic: something that loves water (polar) ● What does selectively permeable mean? the cell membrane only allows certain molecules through ● What does “passive” mean? no energy needed ● What is diffusion? molecules travelling across a membrane from HIGH to LOW concentration ● What is facilitated diffusion? molecules travelling across a membrane from HIGH to LOW concentration with the help of protein channels ● What is osmosis? the movement of WATER across a membrane from HIGH to LOW ○ What happens to a cell in an isotonic solution? stays the same = equal concentration of water inside and outside ○ What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution? shrinks = more water inside the cell, so water will leave it ○ What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution? burst = more water outside the cell, so water will rush in ● What are 2 ways active transport is different than passive transport? active requires ENERGY active goes from LOW to HIGH concentration against the normal concentration gradient ● What is the compound for energy? ATP ● What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis? Endocytosis: bringing something INTO the cell (eating) Exocytosis: something exits or leaves the cell (excreting wastes) EXTRA FOR HONORS: ● Why do scientists think mitochondria were once freeliving organisms? they contain their own DNA and have 2 membranes ● How are the nucleus, ER, and golgi connected? the nucleus assembles ribosomes, which go into the conveyor belt of the ER, attach to the rough ER where the ribosomes start making proteins then the golgi picks up the proteins and ships them around the cell. ● What types of molecules are permeable to the membrane? small molecules: O2, CO2, water ● What types of molecules are impermeable to the membrane? large molecules: glucose, enzymes, nucleic acids ● What is osmotic pressure? when water rushes into plant cells, it increases the pressure inside the cell by filling up the vacuole ● How can plant cells protect bursting open? they have a cell wall for extra support they have the vacuole that stores water and will help to pump water out ● What’s the difference between the 2 types of endocytosis? Phagocytosis: eating large solids Pinocytosis: “drinking” liquids