* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mixed questions
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
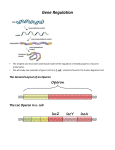
Module 4 1. Provide an overview of the relationship between genotype and phenotype. 2. With the use of a diagram, provide an overview of the general regulation strategies available to a bacterial cell. 3. Feedback inhibition is a reversible and dynamic process. Explain. 4. Compare and contrast repressible and inducible operons. 5. Site 3 examples of global control. Include the system name, environmental signal, the regulatory molecule and its activity and the number of genes regulated. 6. What is catabolite repression and how dies it work? 7. What is Quorum sensing? 8. Chemotaxis is an example of signal transduction. Explain, with the use of diagrams. 9. What are the two main mechanisms by which bacteria regulate enzyme activity and how do they differ? 10. Define the following terms: (a) enzyme (b) active site (c) allosteric enzyme (d) ligand (e) modulator (f) allosteric inhibition (g) competitive inhibition 11. Describe the processes involved in catalysis of a substrate by an enzyme and how competitive and allosteric inhibition affect this catalysis. 12. What role do allosteric effectors play in allosteric inhibition? 13. Allosteric effectors tend to resemble the substrate or products involved in the reactions that they effect. True or false and explain. 14. How do positive and negative allosteric effectors differ? 15. Describe feedback inhibition and give an example where this mechanism is involved in the regulation of a biosynthetic pathway. 16. Explain the central dogma of molecular biology. 17. Gene expression can be regulated at several levels. Explain. 18. Gene expression can be regulated at the levels of transcription and translation. Discuss each with respect to energy efficiency of each mechanism. 19. Define the following terms: (a) operon (b) promoter (c) regulator (d) inducer (e) repressor (f) terminator (g) operator 20. What is autogenous regulation and with what genes is it generally associated? 21. Transcription termination generally involves one of two mechanisms. What are they and which one is used in the regulation of gene expression? 22. What is posttranscriptional regulation and how does it usually work? 23. How does histidine regulate its own synthesis? 24. Corynebacterium glutamicum is used for the commercial production of lysine over other, more highly studied organisms such as E. coli. What elements make it more suited for this purpose than E. coli? (This is a BIG question and requires a BIG answer) 25. Feedback inhibition and repression both play a role in the regulation of lysine biosynthesis in E. coli. True or false and explain. 26. What controls the synthesis of threonine over lysine in Corynebacterium glutamicum? 27. Regulation of aspartakinase can control the production of all the aspartate family of amino acids. Explain. 28. What are the members of the aspartate family of amino acids and why are the classified like this? 29. Explain the regulation of enzymes in the production of lysine and threonine in Corynebacterium glutamicum under the following conditions: (a) high threonine, high lysine (b) high threonine, low lysine (c) low threonine, high lysine (c) low threonine, low lysine 30. What elements make up the lac operon and what roles do they play? 31. The lac operon is an inducible operon. Why and what does this mean? 32. Describe the process of induction in the lac operon. You should discuss both the induced and uninduced states. 33. The lac repressor completely stops transcription of the lac operon structural gene. True or false and explain. 34. The trp operon is an inducible operon. True or false and explain. 35. Describe the process of repression in the trp operon. 36. TrpL does not produce a functional protein. True or false and explain the role of the trpL gene. 37. Explain the process of attenuation in the trp operon under conditions of low and high tryptophan levels. 38. All secondary structures formed in the trp operon attenuator can act as transcription terminators. True or false and explain.