* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of a Cell
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
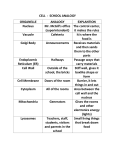
Cells: The Building Blocks of Life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gFuEo2ccTPA What are cells? Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. In other words, cells make up living things and carry out activities that keep a living thing alive. Staying Alive! Cells do MANY things to keep organisms alive, here are a few examples: Break down food for energy Store genetic information Help us grow Reproduction See Smell ETC! What are cells? Cont. A cell is a living thing (you only need one cell to be alive! Unicellular). Cells are able to make more cells like themselves History of Cells I am sure you are all asking yourselves, “who first looked at cells?” Well, thanks for asking, I will tell you. In the 1660’s there was a man named Robert Hooke that lived in Britain and was a scientist. One day Robert Hooke changed some old telescope/microscope blueprints and made a basic light microscope. History of Cells Cont. He used this microscope to see a piece of cork from an oak tree and saw. . . Dun, dun, dun! Cells!!! He thought the cork looked like small rooms (kind of like a hotel with lots of bedrooms) and termed the word cells Plant cells Cork cell Onion cell Elodea cells Animal Cells Blood cells Frog blood cells Cheek Cells The Cell Theory In 1858, after even better microscopes had been invented, Rudolf Virchow developed a hypothesis about cells that has 3 parts. Current Cell Theory Our 1. 2. 3. current cell theory has 3 parts to it: All organisms are composed of cells Cells are alive and the basic living units of organization in all organisms All cells come from other cells Parts of a Cell Just like the atom, a cell has parts, we call these parts organelles. What is an organelle? A part of a cell that performs a specific function Intro to Cells https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZSn03gSqV88 Cytoplasm Function: Contains nutrients for the cell and holds the organelles in place, it is the “squishy insides” Analogy: Think of this as the air that fills up this entire school Cell Membrane Function: Determines what stuff comes in or out, it is the part that surrounds the cell Analogy: Think of this as your school’s entrances and exits Nucleus Function: Directs the activity of the cell via the DNA For example, when it grows and divides DNA tells the cell what type of cell it is Analogy: Think of the principal’s office as the nucleus and the computers as DNA Mitochondria Function: Break down food for energy; known as the “Powerhouse” of the cell Analogy: Think of the lunch room, you eat your food to give you power for the rest of the day Golgi Complex/Apparatus Function: Packages, stores and delivers energy (protein) for the cell Analogy: Think of this as your lunch, it gets packaged/prepared by someone, stored and then you take it out to eat it Endoplasmic Reticulum Function: The “highway” of the cell that moves materials around to other parts Analogy: Think of the school hallways where students and teachers transport ideas to other parts of the school Cell Wall-Only in plants cells, not animals! Function: Provides support to the cells since plants do not have a skeleton Analogy: Think of math, the only subject in our school that has an after school tutor lab! (Math = plant) Chloroplast-found only in plant cells, not animal Function: structures that make food for the plant by converting sunlight into sugar Analogy: Think of a calculator for math, you convert brain waves into answers! Plant Cell https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=uohe2V4yOzE Vacuole-Honors Function: storage for water, nutrients or waste Plant cells have very large ones, animal cells have smaller ones or none at all Analogy: Cupboards and closets where teachers store their stuff Lysosomes-Honors Function: Clean up the cell waste products (Think Lysosomes clean just like Lysol!) Analogy: Think of the janitors who clean up any waste at the school Cell Organelle Song https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=dngsFl2X3nc 1. Which organelle is the highway of the cell? A. Mitochondria B. Nucleus C. E.R. 2. What is the cell membrane’s function A. Allows cell B. materials to enter/exit Contains the DNA C. Cleans up cell waste 3. Which organelle is the powerhouse? A. Lysosomes B. Mitochondria C. Golgi Apparatus 4. The nucleus contains _____, which tells the cell what it is. A. Ribosomes B. Lysosomes C. DNA 5. What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus? A. Packages, energy B. stores, and secretes Controls basic cell processes C. Controls what enters/exits cell Activity Time! Come up with your own cell model or metaphor including all the organelles we have studied today! Some ideas to get you started Organelles Needed Sports -Cytoplasm Mall -Cell Membrane Factory -Mitochondria Restaurant -Golgi Body Country -Nucleus State -E.R. Video Game -Cell Wall (Plants) Etc.! -Chloroplasts (Plants Animal Cell Plant Cell Paper Plate Cell In groups you are going to create a paper plate that compares plant and animal cells. You need to have the following: A realistic 3D representation for each type of cell Labels for each organelle A brief description, in your own words, about what each organelle does I would suggest using a legend or key for your descriptions on a SEPARATE piece of paper