* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic #2 - OCHS Biology
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
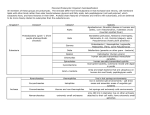
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Name: Period: Date: Honors Biology Topic #2: Domains Archaea and Bacteria 1) Which kingdoms are the ONLY ones that are entirely prokaryotic? Eubacteria and Archaebacteria 2) What does “prokaryotic” mean? a cell without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles 3) How can you remember that these kingdoms are prokaryotic? They both have the word “bacteria” in their names and the only prokaryotic organisms are bacteria. 4) Is it possible for prokaryotic organisms to be multicellular? Why or why not? No, prokaryotic cells are too simple (they do not have mitochondria, chloroplasts, Golgi, ER, etc.). Such simple cells are unable to specialize into specific tissues or work together as a multicellular organism. 5) Can prokaryotes be autotrophic? Yes 6) What does “autotrophic” mean? an organism can make its own food (like through the process of photosynthesis); it does not have to consume other organisms as a food source 7) Can prokaryotes be heterotrophic? Yes 8) What does “heterotrophic” mean? an organism must get its nutrients by consuming other organisms 9) Fill in the Venn Diagram below comparing Archaea and Bacteria. Archaea cell walls have various prokaryotic lipids Bacteria cell walls made of peptidoglycan have a cell wall many are extremophiles cause many common may have flagella illnesses (strep) 10) What is peptidoglycan? molecule made of protein and carbohydrates that makes up the cell wall of bacteria 11) What is an extremophile? An extremophile lives in a very extreme environment, such as high salt, high or low temperature, very acidic, etc. 12) Where would you expect to find a halophile? Acidophile? Thermophile? halophile: very salty environment; acidophile: acidic environment; thermophile: high temperatures 13) Fill in the chart below that distinguishes between the different modes of nutrition possible for Archaea and Bacteria. Photoautotroph Chemoautotroph Photoheterotroph Chemoheterotroph Energy Source? Carbon Source? (Light or chemicals) (CO2 or organic compounds) Light CO2 Chemicals CO2 Light Organic compounds Chemicals Organic compounds 14) Two new prokaryotic species are discovered. One is found in an underwater volcanic vent, the other is found in the small intestine of humans. Which is probably bacteria, and which is probably archaea? the one in the volcanic vent is probably Archaea while the one in the intestine is probably bacteria 15) Look at this labeled image. Briefly describe the purpose of each part of the cell. pili: attachment to surfaces or other cells cell wall: supports the cell Plasmid: contains “special” genes (like antibiotic resistance DNA: carries the genetic material of the cell necessary for it to survive Flagellum: helps the cell move/swim 16) What Domain does the cell to the right belong to? How do you know? Bacteria: it has peptidoglygan cell walls and no nucleus (meaning it is prokaryotic) 17) How would the cell to the right be different if it belonged to the other prokaryotic domain? its cell walls wouldn’t be made of peptidoglycan