* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell plate
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
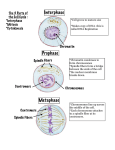
CELL DIVISION Mitosis and Meiosis CELL SIZE Why are cells so small? What causes cells to stop growing and then to divide? CELL SIZE Cell Membrane Size is measure SA (units2) Cytosol Size is measure volume (units3) As cell size increases, the volume increases far more rapidly than SA If SA:V (ie surface area equals volume) becomes too small CELL DUPLICATION Mitosis MITOSIS Growth and repair of plant and animal tissues is due to cell reproduction This reproduction is MITOSIS Continuous process that divides a cell Parent cell divides into two daughter cells Each daughter cell has exactly the same CHROMOSOMES as the parent cell WHAT DOES THIS DIVISION LOOK LIKE? Parent Cell Mitosis Occurs Daughter Cells WHAT DOES CHROMOSOMES LOOK LIKE? THE PHASES OF MITOSIS INTERPHASE Period between cell division 90% of cell’s life Chromosomes are extended into a chromatin network Chromosomes replicate themselves Interphase is over when centrioles migrate to opposite poles PROPHASE Begins when nuclear membrane starts to break down Chromosomes coil into short, thick, clearly visible double stranded chromosomes Astral rays form from centrioles They extend across the cell becoming spindle fibers Prophase is over when the chromosomes begin to move toward the equator of the cell METAPHASE Chromosomes line up beside each other at the equator of the cell Metaphase is over when each centromere of a chromosome attaches itself to a spindle fiber ANAPHASE The chromatids pull apart to move to opposite poles by the shortening of the spindle fibers Ends when the chromatids reach the poles TELOPHASE When the chromatids are at opposite poles the cell can safely divide in two Plant cells and animal cells divide apart in different ways Plant cells, a cell plate forms down the equator Cell plate becomes the missing cell wall if each daughter cell TELOPHASE Animal cells, the cell membrane pinches inward until the two daughter cells separate Each daughter cell then prepares for interphase; chromosomes unwind into a chromatin network, nuclear membranes reform, centrioles move to form a centrosome again, organelles are manufactured to help the new cells grow to mature size DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL MITOSIS: 1. Animal cells use centrioles, plant cells do not 2. Animal cells pinch inwards to separate, plant cells lay down a cell plate to separate Mitosis produces a new cell exactly like the parent cell. How does an organism like a human being develop from a single fertilized egg? Differentiation The process that can change a form from an immature one to a mature one requires 3 different factors: 1. Each type of cell uses only certain info from the chromosomes 2. Neighbouring cells influence each other 3. The cells environment is an influence EX) Scars