* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module A Assessment Anchor A.4 Homeostasis and Transport I
Survey
Document related concepts
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
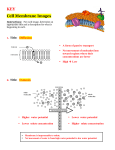
Module A Assessment Anchor A.4 Homeostasis and Transport I. Identify and describe the cell structures involved in transport of materials into, out of, and throughout a cell. a. Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell. i. Plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of 1. Phospholipid bilayer 2. Proteins a. Channel proteins b. Protein pump 3. Cholesterol ii. Membrane is selectively permeable iii. Membrane separates cell from its environment b. Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the plasma membrane. i. Passive transport 1. Diffusion a. Movement of material from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration i. Osmosis movement of water across a membrane from high water concentration to low water concentration 1. Hypertonic-higher solute concentration 2. Hypotonic- lower solute concentration 3. Isotonic-equal solute concentration b. Facilitated diffusion i. Diffusion of material through a protein channel ii. Active transport 1. Pumps a. Move materials from an area of low concentration to area of higher concentration i. Sodium potassium ion pump ii. Contractile vacuole 2. Cytosis a. Movement of larger materials across a membrane i. Endocytosis- movement of materials into the cell 1. Phagocytosis- solid material 2. Pinocytosis- liquid material ii. Exocytosis- movement of materials out of the cell c. Describe how membrane-bound cellular organelles facilitate the transport of materials within a cell i. Golgi apparatus creates vesicles 1. Vesicles will move materials within the cell 2. Vesicles will fuse with membrane to move materials out of the cell II. Explain mechanisms that permit organisms to maintain biological balance between their internal and external environments. a. Explain how organisms maintain homeostasis (constant internal conditions). i. Negative feedback 1. When conditions move outside a set range the organism pushes conditions in the other direction 2. Thermoregulation is an example of negative feedback a. Humans sweat when hot to lower body temperature. ii. Positive feedback 1. Moving conditions away from a set point in a direction 2. Production of clotting material is an example of positive feedback a. Humans will create clotting agents when cut to stop blood loss