* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 34-1 PowerPoint Notes
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
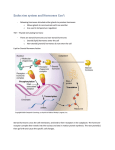
Biologist ___________________________ Date ______________ 34-1 PowerPoint – The Endocrine System Hormones and Glands The endocrine system is like a radio, “________________” chemical messages. These chemicals, called ____________, are released in one part of the body, travel through the blood, and affect cells in other parts of the body. Hormones can affect almost every _______________ in the body. Hormones Hormones act by binding to specific chemical _______________ on cell membranes or within cells. Cells that have receptors for a particular hormone are called _______________ cells. If a cell does not have receptors for a particular hormone, the hormone has ____ effect on it. Hormones Many endocrine functions depend on the effects of ______ opposing hormones, such those shown, to help maintain _______________. Glands A gland is an _______________ that produces and releases a substance, or secretion. _______________ glands release their secretions through tube-like structures (called ducts) out of the body or directly into the digestive system. _______________ glands include those that release sweat, tears, and digestive enzymes. Glands Endocrine glands usually release their secretions (_______________) directly into the blood, which transports the secretions throughout the body. Other body structures, such as bones, fat tissue, the _______________, and the small intestine, also produce and release hormones. Prostaglandins Nearly all cells have been shown to produce small amounts of _______________ substances called prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are modified fatty acids that are produced by a wide range of cells. They generally affect only nearby cells and tissues, and thus are sometimes known as “_______________ hormones.” Hormone Action Hormones fall into two general groups—_______________ and _______________ hormones. Each type of hormone acts on a target cell in a different way. _______________ hormones are produced from a lipid called cholesterol. _______________ hormones include proteins, small peptides, and modified amino acids. Steroid Hormones Because steroid hormones are _______________, they can easily cross cell membranes. Steroid hormones act by entering the _______________ of a cell and changing the pattern of gene expression, making the effects of many steroid hormones especially powerful and long lasting. 1. A steroid hormone enters a cell by passing directly across the cell _______________. 2. Once inside, it binds to a steroid receptor _______________ and forms a hormone-receptor complex. 3. The hormone-receptor complex enters the _______________ of the cell. In the nucleus, it binds to regions of __________ that control gene expression. 4. This binding initiates the transcription of specific genes to _______________ RNA (mRNA). 5. The mRNA moves into the cytoplasm and directs _______________ synthesis. Nonsteroid Hormones Nonsteroid hormones generally _______________ pass through the cell membrane of their target cells. Nonsteroid hormones bind to _______________ in a target cell and cause the release of secondary messengers that affect cell activities. 1. A nonsteroid hormone binds to receptors on the cell _______________. 2. The binding of the hormone activates _______________ on the inner surface of the cell membrane. 3. These enzymes release secondary messengers to relay the hormone’s _______________ within the cell. One common secondary messenger is ____________ (cyclic AMP), which is produced from ATP. Other secondary messengers include calcium ________, nucleotides, and fatty acids. 4. These secondary messengers can _______________ or _______________ a wide range of cell activities. Hormone Action Steroid and nonsteroid hormones can have _______________ effects on their target cells. This makes it especially important to understand the ways in which the _______________ system regulates their production and release into the blood.