* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BF Skinner: Behaviorist He believe behavior is a result of
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Occupational health psychology wikipedia , lookup
Erikson's stages of psychosocial development wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cyberpsychology wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Vladimir J. Konečni wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
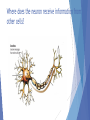
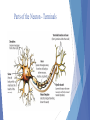
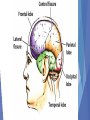
What the different is between cross sectional studies and longitudinal studies? Longitudinal Study: Developmental study where researchers study the same group of individuals for many years. Can be very expensive and difficult to conduct Cross sectional studies: Developmental study where researchers simultaneously study a number of subjects from different age groups and then compare the results. Cheaper, easier than longitudinal studies, but group differences may be due to factors other than development Where does the neuron receive information from other cells? Parts of the Neuron - Terminals Behavior Genetics Perspective: is a mixture of Biological and Behavior perspectives. Nature vs Nurture Focus: How much our genes and environment influence our individual differences. Sample Questions: Does nature (genetics) or nurture (environment) play a more prominent role in our development? Preservation Theory of Sleep: We sleep at night to stay safe and rebuild body. Informational Theory of Sleep: Dreams serve an important memory- related function by sorting and sifting through the day’s experiences BF Skinner: Best known for operant conditioning. Behaviors were dependent upon what happens after the response. Skinner believe behavior is a result of reinforcement or punishment. He did not like punishment. Experimental Group: The subjects in an experiment who are exposed to the treatment (independent variable) Control group: Are not exposed to the independent variable. Results are compared to those of the experimental group In Erikson’s Identity vs. Role Confusion (Adolescence, 13-19 years) search for themselves. They are very self-conscious Freud’s of the psychodynamic psychology: Focus: How behavior springs from unconscious drives and childhood conflicts Freud’s Stages of Development Behaviorist define learning: How we learn to do things or not to do things through reward and punishment? Learning is defined as: A relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Psychoactive drugs: Drugs interfere with normal neurotransmission by Blocking and Binding. THC is the active ingredient in Marijuana: It disrupts memory; lung damage from smoke. Hearing and sight: are two of the senses most affected by old age? Psychology is: The scientific study of behavior and mental processes. Uses scientific research methods. Behavior includes all observable behavior. Mental processes include thoughts, feelings and dreams Piaget stages: Sensorimotor stage: from birth to age two Preoperational stage: starts when the child begins to learn to speak at age two and lasts up until the age of seven Concrete operational stage: from ages seven to eleven. Formal operational stage: from age eleven to sixteen and onwards Amygdala: Two almond shaped structures in the brain that Controls emotional responses such as fear and anger Wilhelm Wundt: is known as the father of psychology because he opened the 1st psychology laboratory. Ethical principles established by the American Psychological Association (APA)? 1. Informed Consent 2. Right to be Protected from Harm and Discomfort 3. Right of Confidentiality 4. Right to Debriefing Kohlberg’s levels of morality? 1. Preconventionl Moral Reasoning: Characterized by the desire to avoid punishment or gain reward 2. Conventional Moral Reasoning: Primary concern is to fit in and play the role of a good citizen 3. Postconventional Moral Reasoning: Characterized by references to universal ethical principles that represent the rights or obligations of all people Humanistic and Psychodynamic psychologist both use “Talk Therapy” to help the sick. Pavlov was a classical conditioning psychologist that is famous for his work with dogs. and his dogs Social Learning Theory: States that people learn from those around them. The culture, the family the school. The central nervous system: The brain and spinal cord. The brain is the location of most information processing. The spinal cord is the main pathway to and from the brain Clinical psychologist Study and treatment of psychological disorders. Diagnose and treat patients with psychological problems Academic Psychologist: Work in Colleges and Universities doing research.