* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Somatotropic axis
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
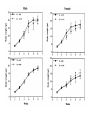
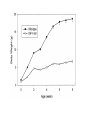
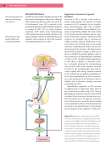
Somatotropic axis Growth hormone • Pituitary protein hormone – 191 amino acids • 22 kDa – Non-glycosylated – Two disulfide bridges • Shares homology with prolactin, placental lactogen, and GHvariant – Gene duplication • Human GH gene – Located in chromosome 17 • 66 kb in length • Cluster of genes that encode closely related genes – GH-V – Placental lactogen/chorionic somatotropins – Transcription of GH mRNA • POUF1 transcription factor – Pituitary specificity – Interacts with protein kinase A pathway Secretion pattern • Pulsatile manner – Interplay between GHRH and SS – Other GH secretagogues – Release of GH in response to GHRH • Elevation of cAMP • GHRH – Critical for development and maintenance of somatotrophs • Hypersecretion results in pituitary tumor development • Role of SS – Affects timing and amplitude of pulsatile GH secretion • Pulsatile GH – Diminished secretion of SS coupled with increased GHRH secretion • Trough GH – Diminished secretion of GHRH coupled with increased SS secretion • Nature of GHRH/SS regulation of GH secretion – Somewhat unclear • Involvement of numerous neurotransmitters Regulation of GH secretion • Major GH pulses (70 % of total daily output) – Slow sleep (deep sleep) – Age-related loss of GH • Decrease quality of sleep • Obesity and diabetes – Decreased GH release – Nutritional status • One of the major regulatory factor of GH secretion • Gender-specific pattern of GH secretion – Affects amount of steroidogenic enzymes • Gender-specific pattern of steroidogenesis – Gender-specific pattern of liver enzyme expression – Gender-specific action of GH • Mediated by STAT 5b activity Effects of growth hormone • Growth of epiphyseal plate in the long bones – Incorporation of sulfur into the epiphyseal cartilage • Sulfation factor • Indirect action of GH (delayed response) – Requirement of mediator(s) • Somatomedins Action of GH • Mediated by Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) – Two types • IGF-I • IGF-II – Structurally similar to preinsulin • Interact with insulin receptor when in high concentrations • IGF-II – Developmentally important – Declines with age – Secretion independent of GH in many species • IGF-I – Mediation of growth – Endocrine • Liver – Local (autocrine/paracrine) IGF-I – Secretion depends on GH • Importance of IGF-I – Total deletion (knockout) • Postnatal lethality – 32-95 % die within 24 hr postpartum – Muscular dystrophy and premature lung development • Growth retardation – Embryonic – Postnatal (35 % less than that of normal) • Infertility – Impaired steroidogenesis • Endocrine IGF-I – Potent inhibitor of GH synthesis and secretion – May not be essential for normal growth • Local IGF-I – Important for normal growth and development – Important for ovarian function • Steroidogenesis – Synergizes with gonadotropins • Cell proliferation