* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
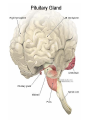
Download Hormones of a pituitary gland
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
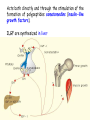
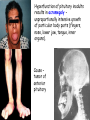
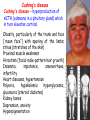
TROPIC HORMONES OF PITUITARY Somatotropic hormone (growth hormone) Chemical nature – simple protein It is secreted continuously during the whole life Secretion is stimulated inhibited by somatostatin by somatoliberin, is Main function – stimulates somatic growth of organs and tissues, particularly bones, cartilages, muscles. Acts both directly and through the stimulation of the formation of polypeptides somatomedins (insulin-like growth factors). ILGF are synthesized in liver The effect of STH on the protein metabolism • Promotes the entrance of AA into cells, • Inhibits catabolism of proteins and AA • Activates the synthesis of proteins, DNA, RNA. The effect of STH on the carbohydrate metabolism Antiinsulin hormone – activates insulinase of liver Activates the exit of glucose from liver Inhibits the conversion of glucose into fat The effect of STH on lipid metabolism Stimulates the decomposition of lipids (lipolisis) Stimulates the oxidation of fatty acids. In the inherited hypoplasia of pituatary gland dwarfism is developed. For the treatment GH is used. Hyperproduction of GH before puberty and before the completion of ossification results in gigantism Yao Defen, the tallest women in the life, 2.36 м Hyperfunction of pituitary inadults results in acromegaly – unproportionally intensive growth of particular body parts (fingers, nose, lower jaw, tongue, inner organs). Cause – tumor of anterior pituitary Adrenocorticotropic hormone (АCTH) Chemical nature – polipeptide Secretion is stimulated by corticoliberin Feedback regulation of the speed of secretion depending on the cortisol level Controls the cortex of epinephrine gland where cortisol is produced: -promotes the increase of cholesterol content in epinephrine glands cortex and its conversion into corticosteroids; -activates the passing of glucose into epinephrine glands and pentose phosphate cycle (NADPH synthesis) -has melanocyte stimulating activity Cushing’s disease Cushing's disease – hyperproduction of ACTH (adenoma in a pituitary gland) which in turn elevates cortisol. Obesity, particularly of the trunk and face (“moon face“) with sparing of the limbs; striae (stretches of the skin) Proximal muscle weakness Hirsutism (facial male-pattern hair growth) Insomnia, impotence, amenorrhoea, infertility Heart diseases, hypertension Polyuria, hypokalemia hyperglycemia, glucosuria (steroid diabetes) Kidney bones Depression, anxiety Hyperpigmentation Thyrotropic hormone (ТТH) Chemical structure – protein (glycoprotein) Secretion is stimulated by thyroliberin The speed of secretion is regulated according to the feedback regulation by thyroid hormones It is necessary for the normal functioning of thyroid gland: -promotes the accumulation of iodine in thyroid gland and its insertion into tyrosine; -stimulates the synthesis of try- and tetraiodthyronin Gonadotropic hormones Follicle-stimulating гормон Chemical nature – protein (glycoprotein) Secretion is stimulated by foliliberin Function: stimulates the function of follicles in women and spermatogenesis in men Luteinizing hormone Chemical nature – protein (glycoprotein) Secretion is stimulated by luliberin Function: stimulates the follicular growth and conversion of the follicle into a corpus luteum n women and secretion of testosterone in men Prolactin Chemical nature – protein Secretion is stimulated by prolactoliberin Functions: -stimulates the function of mammary glands (lactation); -provides the body with sexual gratification after sexual acts -stimulates the function of corpus luteum (progesterone secretion); -stimulates the growth of tissue of prostatic gland in men; -responsible for the mother instinct Lipotropic hormones Chemical nature – simple proteins Functions: -mobilization of lipids from depot; -melanocyte stimulating function; -decrease Ca in blood THE INTERMEDIATE LOBE OF PITUITARY Melanocyte stimulating hormone (melanotropin) Chemical nature – peptide Functions: -stimulates melaninogenesis; -adaptation of vision in darkness POSTERIOR LOBE OF PITUITARY Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) Chemical nature – peptide Functions: -activates hyaluronidase which decomposes hyaluronic acid in the membranes of kidney canaliculi – increases the reabsorption of water in kidneys; -contractions arterioles and capillaries – increases blood pressure Insufficiency – diabetes insipidus (polyuria, low density of urine, dehydratation) Oxytocin Chemical nature – peptide Functions: -stimulates the contraction of smooth muscles (of uterus during labor) -stimulates milk secretion (contraction of muscle fibers around mammary alveoli) Using: -for labor stimulation; -to stop after labor hemorrhage; -for stimulation of milk secretion