* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Psychology Unit 6- Operant Conditioning
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
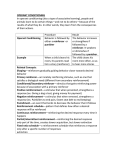
Unit 6: Learning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning • Respondent Behavior: behavior that occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus • Instrumental Learning • Operant Conditioning: A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher • Operant Behavior: behavior that operates on the environment, producing consequences • How is this different from classical conditioning? B. F. Skinner • Law of Effect: Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely • Operant Chamber: aka Skinner Box • Shaping: an operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior • Discriminative Stimulus: A stimulus that elicits a response after association with reinforcement (in contrast to related stimuli not associated with reinforcement) Reinforcements • Reinforcer: Any event that event that STRENGTHENS the behavior it follows • Positive Reinforcement: increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli such as food (any stimulus that, when presented after a response strengthens that response) • Negative Reinforcement: Increasing behavior by stopping or reducing negative stimuli, such as shock (any stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens that response) • Escape Learning • Avoidance Learning Reinforcements • Primary Reinforcers: innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need • Conditioned (Secondary) Reinforcers: stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer; things we learn to value • Generalized Reinforcer: Special kind of secondary reinforcer because it can be paired with other reinforcers and functions as a reinforcer itself • Token Economy • Premack Principle Reinforcement Schedules • Continuous Reinforcement: reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs • Partial (Intermittent) Reinforcement: reinforcing a response only part of the time; results in slower acquisition of a response, but greater resistance to extinction Reinforcement Schedules • Fixed-Ratio Schedules: schedule that reinforcers a response only after a specific number of responses • Variable-Ratio Schedules: schedule that reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses • Fixed- Interval Schedules: schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed • Variable-Interval Schedules: schedule that reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals Punishment • Punishment: an event that decreases the behavior it follows • Positive Punishment: addition of something unpleasant to decrease the behavior it follows • Negative Punishment (omission training): removal of something pleasant to decrease the behavior it follows Extending Operant Conditioning • Cognitive Map: Mental representation of the layout of one’s environment • Latent Learning: Learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it • Insight: A sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem Extending Operant Conditioning • Intrinsic Motivation: A desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake • Extrinsic Motivation: A desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake • Biological Predispositions: animal predispositions constrain the ability to condition; biological constraints predisposed organisms to learn associations that are naturally adaptive • Do you think food is a good reinforcement? How might this be dangerous to people? • Applications • • • • School Work Home Self-Improvement