* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell - Old Saybrook Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
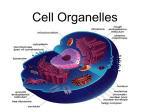
11/12/14 What should you know? The Cell • All of it! Important Players • Robert Hooke (1665) – Coined the term “cell” • Anton van Leeuwenhook (1674) – “animalcules” • Matthias Schleiden (1838) – All plants made of cells • Theodor Schwann (1839) Cells are bitchin’ Animalcules YAY! The Cell Theory • All livings things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living things • New cells are produced from existing cells – All animals made of cells • Robert Virchow (1855) – All cells come from cells What do all cells have in common? • Cell membrane – Thin, flexible barrier – “Gatekeeper” • Hereditary material – DNA • Cytoplasm – Fluid within the cell • Organelles-not membrane bound in prokaryotes – Helps the cell to function Two categories of cells Prokaryote • No nucleus • No membrane covered organelles • Circular DNA • Bacteria • Less DNA • Always cell wall • Older • Simple • Smaller Eukaryote • Nucleus • Membrane covered organelles • Linear DNA • All other cells • More DNA • Sometimes cell wall • Younger • Complex • Bigger 1 11/12/14 Cell Structures • • • • • • • • • • • • • Cell Wall • Lies outside the cell membrane • Allows H2O, O2 and CO2 to pass • Main function is to provide support and protection • Compose of CHO and protein Cell wall Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear envelope Cytoskeleton Centriole Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Chloroplast Mitochondria Cell wall vs no cell wall Cell Wall Cell Membrane – Plant cell walls = cellulose Nucleus • Controls most cell processes • Contains DNA • Chromatin/Chromosomes • Nucleolus • Nuclear envelope Hereditary Information • Chromatin – DNA bound to protein, granular material visible in nucleus • Chromosome – condensed chromatin apparent when cell divides 2 11/12/14 Nucleolus Nuclear envelope • Small dense region within the nucleus • Where ribosomes are assembled • Double membrane layer surrounding nucleus • Sprinkled with nuclear pores – Allows material to move in and out of nucleus Nuclear Envelope Cytoskeleton Microtubule • Network of protein filaments that help the cell to maintain its shape • Aids in cell movement • Composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments • Hollow tubes of protein • Maintain shape • Allow a “track” for organelles to travel on • Help to separate chromosomes during cell division – Centrioles (animals only) • Cilia & flagella Intermediate & Microfilament Cytoskeleton • Long, thin fibers • Help cell movement • Smaller than microtubule • Provide tough flexible framework that supports the cells Microfilament 3 11/12/14 Organelles in the cytoplasm • • • • • • • • Ribosome • Protein assembled on ribosome Ribosomes ER Golgi apparatus Centriole Lysosme Vacuoles Chloroplast Mitochondria ER – act as a transport system • Smooth ER Golgi Apparatus • Proteins made by rough ER are sent here where CHO and lipids attached – Components of cell membrane assembled here – Prepared to be sent to their final destination • Rough ER – Proteins are modified “spell check” Golgi Lysosomes The “Suicide Sac” • Organelle filled with enzymes – Break down lipids, CHO, and proteins from food into particles that can be used by the cell – Break down old organelles • Only found in animal cells 4 11/12/14 Centriole • Found within the centrosome – Area where microtubules are produced • Aid in cell division by helping to move chromosomes by organizing spindle • ONLY ANIMAL CELL Vacuoles • Structure used to store water, salts, proteins, CHO • Plants have a single large vacuole • Contractile vacuole – Squeezes out extra water in aquatic unicellular organisms Chloroplast Mitochondria • Not in animal and fungal cells • Site of photosynthesis • Two envelope membrane • Stacks of photosynthetic “coins” • Chlorophyll • Use energy from food to make ATP – Growth – Development – Movement • Two membranes Endosymbiotic Theory • Eukaryotes evolved by a large prokaryotic cell engulfing mitochondria and chloroplasts • Evidence: By Lynn Margulis – contain their own DNA necessary for their proper function – Contain ribosomes – Reproduce via binary fission 5 11/12/14 Animal • Lysosome • Centriole • Small vacuole Small Vacuole Cell Categories Plant • • • • Cell wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast Large vacuole PROKARYOTIC EURKARYOTIC Animal Plant Lysosome Another look 7 8 10 9 11 How much do you know? 6