* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
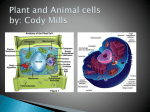
:::Index> The Secret Garden of Genetics>Knowledge Acquisition>Origin of Life>The Basic Unit of Organism The Basic Unit of Organism 【Cell Function】 Cells are usually very small and are made up of various shapes and different functions, e.g. the epidermal cells in the skin are flat and arranged compactly; erythrocytes are biconcave shaped and capable of transporting oxygen; nerve cells have many spikes and are able to transmitting signals. 【Cell Structure】 Cells are the most basic units to constitute an organism and classified into many categories, but are basically made up of a cell membrane, a cytoplasm and a nucleus. In addition, there exist some different characteristics between animal cells and plant cells, i.e. plant cells have vacuoles, cell walls and chloroplasts, and animal cells have lysosomes and centrioles. Fig.1:The main components of the animal cell Nucleus:If we compare fruits of peaches and plums to cells, the location of nucleus is the same as that of the kernels in peaches and plums. A nucleus has a cell blueprint All rights reserved by National Taiwan Science Education Center and is made up of chromosomes and DNA molecules. A cell must set up its shape and control activities via the blueprint. Cell membrane:It constitutes the outer layer of cells and is one kind of lipids in essence. The cell membrane can control the cell substance tranportation. Cytoplasm:It is made up of a colloidal matrix. The cytoplasm is diffused between the nucleus and the cell membrane and contains many organelles. Mitochondrion:It is made up of a bi-layer membrane; the outer membrane is smooth and the inner membrane protrudes inwards to form many infoldings. These infoldings are involved in cell respiration and act as a generator to produce ATP(energy) for cell operation. Endoplasmic reticulum:They are classified into rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is like an industrial conveyor belt which can transport substance; the smooth endoplasmic reticulum can produce steroid hormones. Golgi body:They are adjacent to the nucleus and formed by the stack of many flat sac membranes, acting as an industrial cutting device which can modify produced proteins and make them function. Cell wall:It encloses the outside of the cell membrane and is made up of cellulose which can protect cells and maintain their shapes. Chloroplast :It is made up of bi-layer membranes and involved in photosynthesis, acting as a solar cell which can absorb sunlight and generate energy. Vacuole:It is located at the centre of plant cells. The vacuole can store water and produce turgor pressure to maintain the cell shape. All rights reserved by National Taiwan Science Education Center Reviewed by:Zhang, Yong-Ta professor All rights reserved by National Taiwan Science Education Center