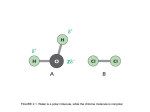
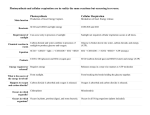
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EOC in class Study Guide
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Unit 1 Summary 1.The work of scientists usually begins with a. testing a hypothesis. b. careful observations. c. creating experiments. d. drawing conclusions. ____ 2. A student suggests that a certain species of bacteria grows better in the light than in the dark. The student has 10 culture plates on which to grow the bacteria. Which of the following would be the best experiment to test this idea? a. Grow 10 plates in the dark. b. Grow 10 plates in the light. c. Grow 5 plates in the dark and 5 plates in the light. d. Grow 10 plates in the light, with extra water. ____ 3. Which is NOT a unit of measurement in the metric system? a. meter b. inch c. kilometer d. gram ____ 4. Because you may come in contact with organisms you cannot see, what safety procedure MUST be followed? a. Read over your activity. b. Open the windows of the laboratory. c. Wash your hands thoroughly after completing the activity. d. Do not wear long sleeves. Unit 2 Summary _____ 5. The three particles that make up atoms are a. protons, neutrons, and isotopes. b. neutrons, isotopes, and electrons. c. positives, negatives, and electrons. d. protons, neutrons, and electrons. ____ 6. If an atom contains 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons, its mass number would be a. 3. b. 4. c. 7. d. 11. ____ 7. A monosaccharide is a a. carbohydrate. b. lipid. c. nucleic acid. d. protein. ____ 8. A substance that accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction is called a(an) a. catalyst. b. lipid. c. molecule. d. element. Unit 3 Summary ____ 33. Which of the following is a function of the nucleus? a. stores DNA b. controls most of the cell’s processes c. contains the information needed to make proteins d. all of the above ____ 36. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a. an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. b. an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. c. an area of equilibrium to an area of high concentration. d. all of the above ____ 37. When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same, the molecules will a. move across the membrane to the outside of the cell. b. stop moving across the membrane. c. move across the membrane in both directions. d. move across the membrane to the inside of the cell. ____ 38. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? a. diffusion b. osmosis c. facilitated diffusion d. active transport ____ 39. An animal cell that is surrounded by fresh water will burst because the osmotic pressure causes a. water to move into the cell. b. water to move out of the cell. c. solutes to move into the cell. d. solutes to move out of the cell. Unit 4 Summary ____ 9. What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? a. adenine, thylakoids, stroma b. stroma, grana, chlorophyll c. adenine, ribose, phosphate groups d. NADH, NADPH, and FADH2 ____ 10. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions? a. oxygen gas b. ATP c. NADPH d. all of the above ____ 11. What is the correct equation for cellular respiration? a. 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy b. 6O2 + C6H12O6 + Energy 6CO2 + 6H2O c. 6CO2 + 6H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 + Energy d. 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 ____ 12. How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis almost opposite processes? a. Photosynthesis releases energy, and cellular respiration stores energy. b. Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back. c. Photosynthesis removes oxygen from the atmosphere, and cellular respiration puts it back. d. all of the above Unit 5 Summary ____ 17. Which of the following is a nucleotide found in DNA? a. ribose + phosphate group + thymine b. ribose + phosphate group + uracil c. deoxyribose + phosphate group + uracil d. deoxyribose + phosphate group + cytosine ____ 18. In eukaryotes, DNA a. is located in the nucleus. b. floats freely in the cytoplasm. c. is located in the ribosomes. d. is circular. ____ 19. During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand with the bases a. TCGAAC. b. GATCCA. c. AGCTTG. d. GAUCCA. ____ 20. Which of the following are found in both DNA and RNA? a. ribose, phosphate groups, and adenine b. deoxyribose, phosphate groups, and guanine c. phosphate groups, guanine, and cytosine d. phosphate groups, guanine, and thymine ____ 21. How many bases are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 3 b. 6 c. 9 d. 12 Unit 6 Summary ____ 40. The process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells is called a. cell division. b. metaphase. c. interphase. d. mitosis. ____ 41. Which of the following represents the phases of mitosis in their proper sequence? a. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase b. interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase c. interphase, prophase, metaphase, telophase d. prophase, anaphase, metaphase, telophase ____ 42. Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost the ability to control their a. size. b. spindle fibers. c. growth rate. d. surface area. Unit 7 Summary ____ 14. The principle of dominance states that a. all alleles are dominant. b. all alleles are recessive. c. some alleles are dominant and others are recessive. d. alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. ____ 15. A heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a short plant. The probability that an F1 plant will be tall is a. 25%. b. 50%. c. 75%. d. 100%. ____ 16. If an organism’s diploid number is 12, its haploid number is a. 12. b. 6. c. 24. d. 3. Unit 8 Summary ____ 22. When lions prey on a herd of antelopes, some antelopes are killed and some escape. Which part of Darwin’s concept of natural selection might be used to describe this situation? a. acquired characteristics b. reproductive isolation c. survival of the fittest d. descent with modification ____ 23. The number and location of bones of many fossil vertebrates are similar to those in living vertebrates. Most biologists would probably explain this fact on the basis of a. the needs of the organisms. b. a common ancestor. c. the struggle for existence. d. the inheritance of acquired traits. ____ 24. The same kinds of cells that grow in similar patterns in different but related organisms produce a. homologous structures such as wings and arms. b. the same kind of embryos. c. natural variations in a population. d. descent with modification. Unit 9 Summary ____ 25. The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called a. economy. b. modeling. c. recycling. d. ecology. ____ 26. What is the original source of almost all the energy in most ecosystems? a. carbohydrates b. sunlight c. water d. carbon ____ 27. What is the term for each step in the transfer of energy and matter within a food web? a. energy path b. food chain c. trophic level d. food pyramid ____ 28. Nitrogen fixation is carried out primarily by a. humans. b. plants. c. bacteria. d. consumers. ____ 29. The greenhouse effect is a. the result of an excess of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. b. a natural phenomenon that maintains Earth’s temperature range. c. the result of the differences in the angle of the sun’s rays. d. an unnatural phenomenon that causes heat energy to be radiated back into the atmosphere.