* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
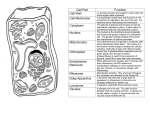
Cells The place where life begins What is a cell? • A cell is the smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms – This means that cells make up all living things! • An organism is any living thing – All organisms are made up of cells Itty bitty cells • Most cells are too small to see with your eyes alone • Why are they so small? – Cells are limited by their surface area – Cells take in nutrients and get rid of waste through their surface – If it’s volume grows too big, there will not be enough surface area to pass nutrients and waste through Cell Theory • All organisms are made up of one or more cells • The cell is the basic unit of all organisms • All cells come from existing cells Three important people to cell theory Anton van Leeuwenhoek • Saw cells from pond water under a microscope • Contributed to the first part of cell theory Theodor Schwann Rudolf Virchow • Determined animals were made of cells after Matthias Schleiden determined plants were made of cells • Concluded all organisms are made of cells • Concluded that the cell is the basic unit of life • Proposed that cells could only form from the division of other cells • Responsible for the 3rd part of cell theory Important Vocab • Unicellular organism- 1 cell carries out all functions of life • Multicellular organism – cells have specialized functions and work together for the good of the organism What do all cells have in common? • Cell membrane- a protective layer that convers the cells surface – Acts as a barrier – Controls movement of materials in and out of the cell • Cytoplasm- the area inside of the cell – Fluid – Contains the organelles Continued • Organelle- small “bodies” in the cell used to preform specific functions • DNA – provides the codes for the instruction of all cell processes – Usually found in a membrane bound organelle called the nucleus 2 Types of Cells Prokaryotic • NO nucleus or membrane bound organelle • DNA is located in the cytoplasm • Contain ribosomes • Some contain flagella – Hair-like structures for movement • Smaller than Eukaryotes • Bacteria and Archaea Eukaryotic • Contain a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles as well as ribosomes • Not all the same • Make up animals, plants, protists, and fungi • All multicellular organisms have eukaryotes • Can be unicellular