* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA, RNA, and GENES
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
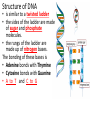
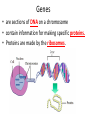
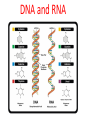
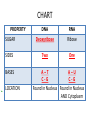
DNA, RNA, and GENES Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid • DNA is a Chemical code that contains information that an organism needs to grow and function (nucleic acids) History • Watson and Crick made an accurate model of DNA in 1953. • Chargaff discovered the pattern found in the nitrogen bases. • Rosalind Franklin discovered shape of DNA. Structure of DNA • is similar to a twisted ladder • the sides of the ladder are made of sugar and phosphate molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G • Before a cell divides, its DNA duplicates itself by unwinding and separating its sides, then forming new identical DNA. Genes • are sections of DNA on a chromosome • contain information for making specific proteins. • Proteins are made by the ribosomes. Ribonucleic Acid • RNA carries the code for making proteins from the nucleus to the ribosome. • Unlike DNA which has 2 sides, RNA has ONE side. • RNA has the base URACIL instead of thymine. Types of RNA • Messenger RNA carries the code for the order in which the amino acids bond. • Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes, where proteins are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. • Cells use only the genes that direct the making of proteins needed by that cell. • Cells must be able to control genes by turning some genes on and some off. DNA and RNA CHART PROPERTY SUGAR SIDES BASES LOCATION DNA Deoxyribose RNA Ribose Two One A–T A–U C-G C-G Found in Nucleus Found in Nucleus AND Cytoplasm Mutations • Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence of a cell’s gene or chromosome. • Mutations can be caused by outside factors like X-rays, sunlight, and chemicals. • A change in gene or chromosome can change the traits of an organism. Answers to DNA-Double Helix sheet 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Nucleus Watson and Crick Like a twisted ladder Sugars and phosphate Amino acids (nitrogen bases) Deoxyribose Nucleotides