* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aerobic vs. Anaerobic respiration
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
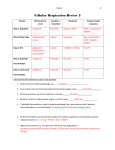
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic respiration Objectives: Review the two types of anaerobic respiration. Explain the specific steps of alcohol & lactic acid fermentation. Compare & contrast aerobic & anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen. Oxygen present Alcohol fermentation converts pyruvate into ethyl alcohol. Glucose NAD+ 2 ATP 2 Pyruvate NADH e CO2 C 2 Ethyl alcohol NAD+ Yeast use alcohol fermentation to break down glucose when oxygen is absent. Produces CO2 and alcohol Live yeast: undergoing anaerobic fermentation Breaking down glucose to form 2ATP Dead yeast: cannot undergo anaerobic fermentation Proteins necessary for reaction broken down due to change in temperature. Enzymes (proteins) only work at specific temperatures! Alcohol fermentation is used to make wine, beer, & bread. CO2 helps bread rise Alcohol production for wine & beer Glycolysis does not require oxygen. Glucose NAD+ 2 ATP 2 Pyruvate NADH When O2 continues on with cellular respiration to be converted into Acetyl CoA When oxygen is absent, anaerobic respiration occurs. Two types: Alcohol fermentation Lactic acid fermentation Both utilize glycolysis to produce ATP Make very little ATP, 2 per glucose Lactic acid fermentation turns pyruvate into lactic acid. Glucose NAD+ 2 ATP 2 Pyruvate NADH e 2 Lactic acid NAD+ Lactic acid fermentation causes muscles to burn during exercise. • When exercise too much or too quickly muscles use lactic acid fermentation. • Build up of acid causes muscles to burn. • Occurs in animals Similarities & differences between anaerobic aerobic respiration. Anaerobic Uses glycolysis to produce ATP Produces 2 ATP per glucose Does not require oxygen Occurs in prokaryotes Aerobic Uses glycolysis, Kreb cycle, & electron transport chain to produce ATP Produces 32-38 ATP per glucose Requires oxygen Occurs in eukaryotes Key points Anaerobic respiration can be used when oxygen isn’t available to allow production of ATP. Anaerobic respiration has many commercial applications. Aerobic respiration is more efficient at producing ATP but its requires oxygen.