* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleic Acids
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
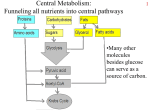
Fermentation Chapter 9 What you need to know! • The difference between fermentation and cellular respiration. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic • Aerobic = with air – Aero is Greek for air – Air = oxygen • Anaerobic = without air – An as a prefix means no; An (no) aero (air) • Aerobic respiration = cellular respiration • Anaerobic respiration = fermentation Fermentation • Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that yields ATP during fermentation – Yields: Write the products of glycolysis here • Eventually a cell will run out of NAD+ – No more glycolysis • Fermentation recycles the NADH back into NAD+ Types of Fermentation 1. Lactic acid fermentation: – – – – NADH NAD+ Pyruvate lactate (lactic acid) Causes muscle soreness Filtered by the liver 2. Alcohol fermentation – NADH NAD+ – Pyruvate CO2 & ethanol (ethyl alcohol) – CO2 puts bubbles in beer and champagne and makes dough rise Types of Fermentation ATP Yield • Anaerobic yields 4 ATP during glycolysis – 2 ATP activation cost • Net Gain 2 ATP • Aerobic yields 40 ATP during all 3 steps – 2 ATP activation cost • Net Gain 38 ATP • Aerobic respiration is 19 X’s more efficient per glucose molecule Various Metabolisms • Obligate (strict) aerobes – Organisms that require oxygen to survive – Ex: all vertebrates • Facultative anaerobic organisms – Can do aerobic or anaerobic cellular respiration (CR) depending on the situation – Ex: yeast, muscle cells • Obligate (strict) anaerobes – Require oxygen free environment (die in the presence of O2) – Ex: deep soil and stagnant pond bacteria Food • Not everything you eat is broken down into glucose • Fat yields double the ATP of carbs • Food also provides essential bio-chemicals for growth