* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Osmosis Experimental Design Lab
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
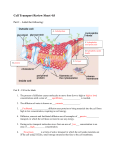
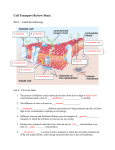
Osmosis Experimental Design Lab Background: Recall from discussions in class that cells use transport methods such as diffusion, osmosis, and active transport to allow substances to cross their cell membrane. Some transport methods are considered passive because they do not require the cell to expend any energy. Other transport methods are active because they require the cell to expend energy. In this lab, you will be investigating osmosis, the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane. Three types of solutions can surround a cell: hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic. A hypertonic solution has more dissolved substances than inside the cell. A hypotonic solution has less dissolved substances than inside the cell. An isotonic solution has the same concentration of dissolved substances as inside the cell. The type of solution that surrounds a cell will influence the net flow of water and substances into and out of the cell. Pre-Lab Questions: 1. Diffusion is the net movement of substances from an area of _____________ concentration to an area of _______________ concentration. 2. A cell’s membrane is semi-permeable (also called “selectively permeable”). What does this mean? 3. If a cell is in a hypertonic solution, what is the direction of the net flow of water and why? 4. If a cell is in a hypotonic solution, what is the direction of the net flow of water and why? 5. If a cell is in an isotonic solution, what is the direction of the net flow of water and why? Problem Statement In this lab, you will observe the process of diffusion and osmosis. Two labs will help demonstrate these processes. Hypothesis What do you think will happen to the potato slices in the water, the salt water, and the open air? What do you think will happen to the balloon filled with vanilla in the Ziploc bag? Materials 3 Potato slices 3 Jars/Beakers Timer Balloon Vanilla Ziploc Bag Pipette Procedure 1. Feel the texture of the potato slices. Place one slice into a beaker of fresh water, one slice into the beaker with salt water, and leave the third slice exposed to the air. Wait 20 minutes. 2. Place 10 drops of vanilla extra inside a deflated balloon. Make sure not to get any vanilla on the outside of the balloon. Inflate the balloon to a size that will easily fit into the plastic bag and seal the bag. Wait 20 minutes. 3. After the 20 minutes, feel the texture of the three potato slices and record your observations. 4. Open the Ziploc bag and smell the air inside the bag by wafting. Record your observations. 5. Leave the bag open and smell the bag two minutes later. Record your observations. Data Collection Smell of bag Smell of bag (2 minutes later) Potato in Water Potato in Salt Water Potato in Air Potato Analysis 1. The texture of the fresh potato slice is turgid, in between, or flaccid? 2. What happened to the water in the potato when it was soaked in the water solution? 3. What happened to the water in the potato when it was soaked in saline solution? 4. Comparing the potato exposed to water and the potato soaked in saline solution. Which texture is more turgid? Why? 5. Plant cells use the central vacuole to provide support for their cell walls. When the flank becomes turgid, what is happening inside the cell? 6. What type of solution was the water solution? The salt solution? Vanilla Balloon Analysis 7. After the twenty minutes, did it smell inside the bag? 8. How did the smell get into the bag? 9. After the bag was open for two minutes, was the smell more or less concentrated compared to when you first opened it? Why? Conclusion Questions 10. Were your predictions correct? If they were not correct, why do you think there was a difference between your predictions and what you observed during your experiment? 11. What do your results teach you about the effects of osmosis across a semi-permeable membrane? 12. Explain what happens to an animal cell that is placed in a hypertonic solution vs. a hypotonic solution. 13. Explain what happens to a plant cell that is placed in a hypertonic solution vs. a hypotonic solution. 14. What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion? How does diffusion use concentration gradients?