* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polygenic and Multifactoral Traits
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of autism wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
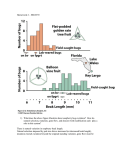
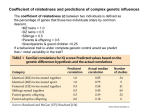
Polygenic and Multifactoral Traits • Polygenic inheritance Continuous variation Additive alleles Calculating the number of genes • Heritability Statistical tools: Mean, variance Broad sense heritability Narrow sense heritability Twin Studies and concordance Continuous variation • Kolreuter’s cross • Dwarf x tall tobacco • F1 intermediate • F2 intermediate, normal distribution Multiple gene hypothesis • East’s cross of Nicotiana with different corolla length • Indicates Mendelian segregation of different phenotypic classes • Took subsets of F2 and crossed. Multiple factor hypothesis • • • • • • Characters quantified Two or more genes Additive alleles Contribute a constant amount Non-additive add nothing All alleles add equally Polygenic inheritance • 2 or more genes • Show continuous variation vs discontinuous • Additive component • Distinct phenotypic classes • Quantitative traits: size, weight, height,IQ Polygenic inheritance Skin color Additive Model • (1/4)n= ratio of f2 individuals showing extreme phenotype • n = (2n +1) phenotypic classes Regression to the mean • Tendency of offspring of parents with extreme differences in phenotype to exhibit a phenotype that is average of the two parental phenotypes • Dominant and additive effects Threshold effects • Some individuals show affected or unaffected phenotypes • Predisposition is caused by a number of genes in an additive way • Will develop the genetic disorder if exposed to proper environmental conditions. Familial Risks • First degree: Parentchild share ½ genes • Second degree: grandfather: grandchild share ¼ genes • Third degree share 1/8 genes Statistical Analysis • Mean (X) = ∑Xi/n • Variance (s2) = (∑Xi – X)2/n-1 • Standard deviation (s) = √s2 Broad-sense Heritabilty • H2 = proportion of total variance caused by genetic variance • H2 = 1.0, all genetic • H2 = 0 all variation due to environment • Vp= phenotypic var • Vg= genetic var • VE= enviromental var • Vp= Vg + VE • H2= Vg/Vp Twin studies Heritability Survey of traits