* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Unit Review Robert Hooke They turn genes (directions in the
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
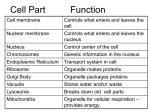
Name: ________________ Cell Unit Review 1. Which scientist was among the first people to see and describe cells according to the cell theory? Robert Hooke 2. What do cells do to their genes to become specialized? They turn genes (directions in the nucleus) on and off. 3. What are the functions of proteins in the cell membrane? Identify the cell and act like tunnels or pumps through the cell membrane. 4. List the three statements that are usually part of cell theory. o All living things are made of cells. o Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. o Living cells come only from other living cells. 5. Which organelle is found on the ER and is a tool for putting proteins together? ribosomes 6. What does ER stand for? Endoplasmic reticulum (just be able to recognize it from the test, not spell it ) 7. What is usually stored in vacuoles in the cell? Water, food, waste, cell products 8. What does a lysosome contain? enzymes 9. What is the function of the Golgi Complex? Modify proteins and pack them into vacuoles or vesicles 10. Name an organelle to go with each statement below: ______Mitochondria_____ these organelles take in sugar and release the energy from it so other cells can use it, kind of like a little power plant inside the cell ______Chloroplasts______ these are filled with chlorophyll to trap energy from the sun and store it as sugar, known as the site of photosynthesis ______Cell Membrane_____ this part holds the cell together and controls what gets into the cell and what is let out of the cell _____Cytoplasm_____ made of mostly water and some dissolved materials, this gel inside the cell surrounds the organelles ______Cell Wall_____ made of carbohydrates like cellulose, this outer layer protects a cell like a suit of armor. _____Nucleus_____ this organelle is the control center for the cell because it holds the chromosomes, which are the directions for how to make all the cell’s parts 11. Do the cells from the inside of your cheek have a visible nucleus? Yes! (the blue dot in the middle when we saw them under the microscope) 12. What types of cells have both a cell membrane and a cell wall? Plant cells, fungus cells, many bacteria and protists 13. What types of cells have chloroplasts? Green parts of plants and some protists 2 14. What is the name of the reaction that releases energy from sugars and puts the energy into a form that cells can use? Respiration 15. What function can cilia and flagella both help cells to do? Swim (or move) 16. Are the directions (chromosomes) in each of your cells the same? Yes. How do these directions control what types of products each cell makes? They are turned on and off. (remember the genes for making hair are turned off in your eyeball cells ) 3 Draw a cell and include in your sketch each of the following cell parts. Make sure to label each one. Cell Membrane Cilia Cytoplasm ER Flagellum Mitochondria Nucleus 4 Fill in the blanks in the list below using the word bank. Biosphere Biome Ecosystem Community Population Organism Organ System Organ Tissue Word Bank Atom Biome Biosphere Cell Ecosystem Macromolecule Molecule Organ Organ System Organelle Organism Population Community Tissue Cell Organelle Macromolecule Molecule Atom 5